How to Mask Sensitive Data in MySQL
MySQL powers everything from customer-facing applications to analytics pipelines and internal reporting. That flexibility is also why sensitive data leaks happen: production records get copied into dev/test, shared with vendors, or exposed through BI exports. Masking reduces that risk by transforming sensitive values into safe substitutes while keeping schemas and queries usable.
Data masking protects Personally Identifiable Information (PII), payment data, and regulated fields without blocking legitimate workflows. In MySQL, masking typically falls into three modes: dynamic data masking, static data masking, and in-place masking.
Step 1: Identify Sensitive Data in Your MySQL Schema
Start by defining what “sensitive” means for your system. Common MySQL sensitive data includes PII such as names, emails, phone numbers, addresses, and government identifiers. Many organizations also classify salary, customer IDs, and internal financial attributes as sensitive.
Make identification repeatable. Use a structured data discovery process and align the results with your data security policy and compliance regulations. This is the foundation for consistent policy enforcement and audit evidence.
Step 2: Choose the Right Masking Strategy
Most teams mix masking approaches based on environment and audience:
Dynamic masking: Masks results at query time, so production data remains unchanged. Use it for support, analysts, and read-only roles.
Static masking: Produces a masked copy for dev/test or sandboxes where real identifiers aren’t required.
In-place masking: Permanently de-identifies values in a target environment (for example, long-lived non-production databases).
When selecting the approach, decide the masking style you need: full redaction, partial reveal (for example, last 4 digits), or deterministic substitution for analytics. Deterministic masking preserves joins and grouping but increases re-identification risk, so it should be paired with access control and monitoring. Randomized masking is safer for exports, but it can break correlation and test cases. Balance usability and risk based on your data security priorities and the goal of database security.
If you need a quick reference for typical transformations and trade-offs, see masking types.
Start with discovery and classification, then apply dynamic masking to production read access and static masking for dev/test copies. This reduces risk quickly without breaking workflows.
Step 3: Native MySQL Masking Options
You can implement basic masking directly in MySQL, but you must design it carefully to avoid bypass.
View-based masking
Views can expose masked projections and keep raw tables restricted. This works well for stable reporting. However, it relies on strict access control. MySQL view syntax is documented here: CREATE VIEW statement.
-- Masked projection via a view (example only)
CREATE VIEW v_customers_masked AS
SELECT
id,
CONCAT(LEFT(full_name, 1), '***') AS full_name,
CONCAT(LEFT(email, 1), '***@', SUBSTRING_INDEX(email,'@',-1)) AS email,
CONCAT('***', RIGHT(phone, 2)) AS phone,
CONCAT('XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-', RIGHT(credit_card, 4)) AS credit_card,
address,
salary,
created_at
FROM customers_sensitive;
GRANT SELECT ON v_customers_masked TO 'report_user'@'%';
REVOKE SELECT ON customers_sensitive FROM 'report_user'@'%';
To reduce bypass risk, enforce role-based access control (RBAC) and the principle of least privilege so users can’t access underlying tables.
Enterprise masking functions
Some organizations use MySQL Enterprise data masking and de-identification functions. Validate edition and version support in the official reference: MySQL data masking and de-identification functions.
Step 4: Mask Sensitive Columns in MySQL with DataSunrise
When you need centralized masking policies across BI tools, admin consoles, and scripts, a dedicated policy layer is usually the simplest approach. DataSunrise provides a unified database security layer. In many environments it operates as a reverse proxy, applying masking consistently without application changes.
1) Create a dynamic masking rule and attach the MySQL instance
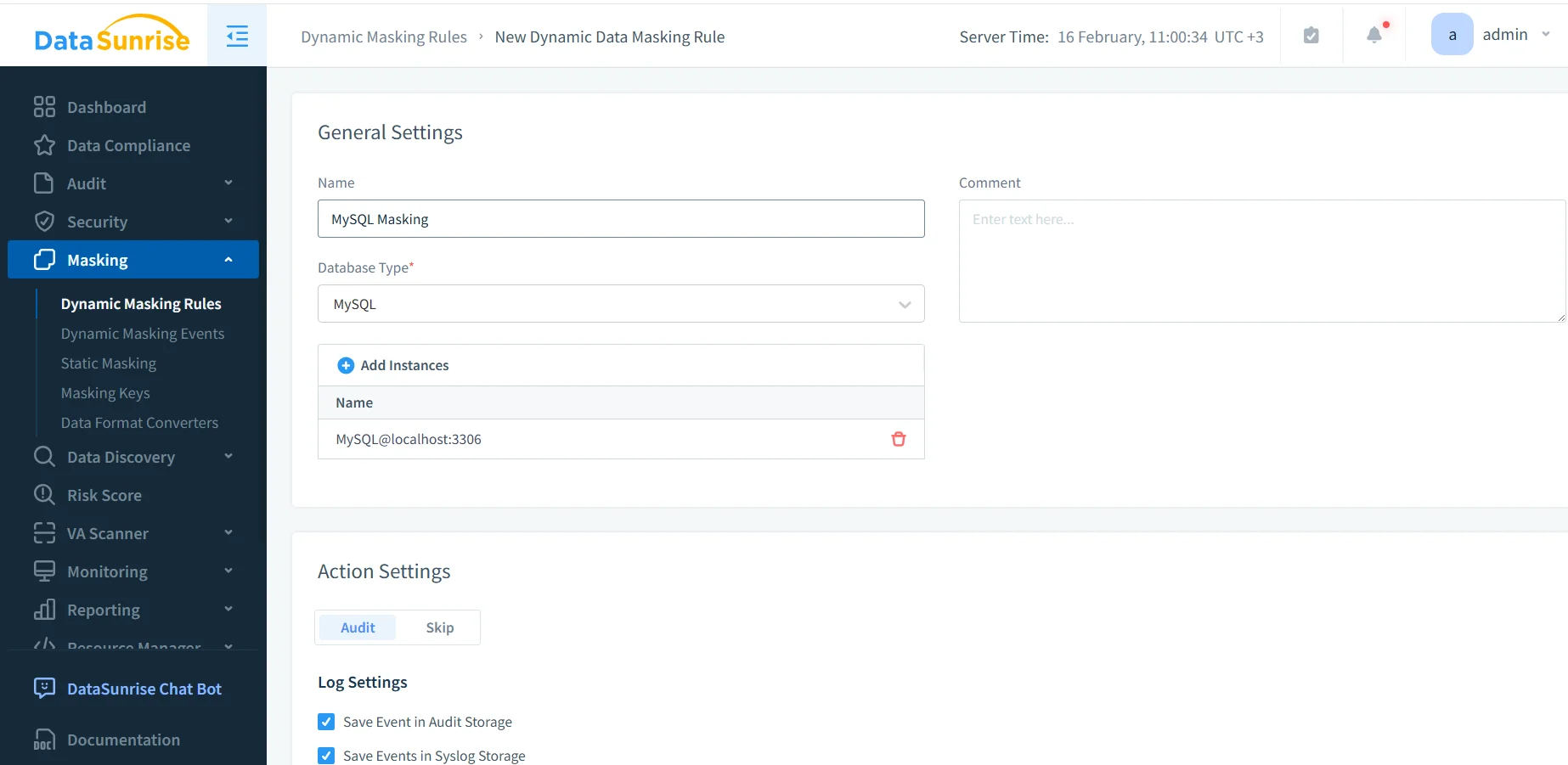
Define the rule name, choose MySQL as the database type, and select the instance. Pair masking with access controls so policy decisions are consistent across roles and tools.
2) Select schemas, tables, and columns to mask
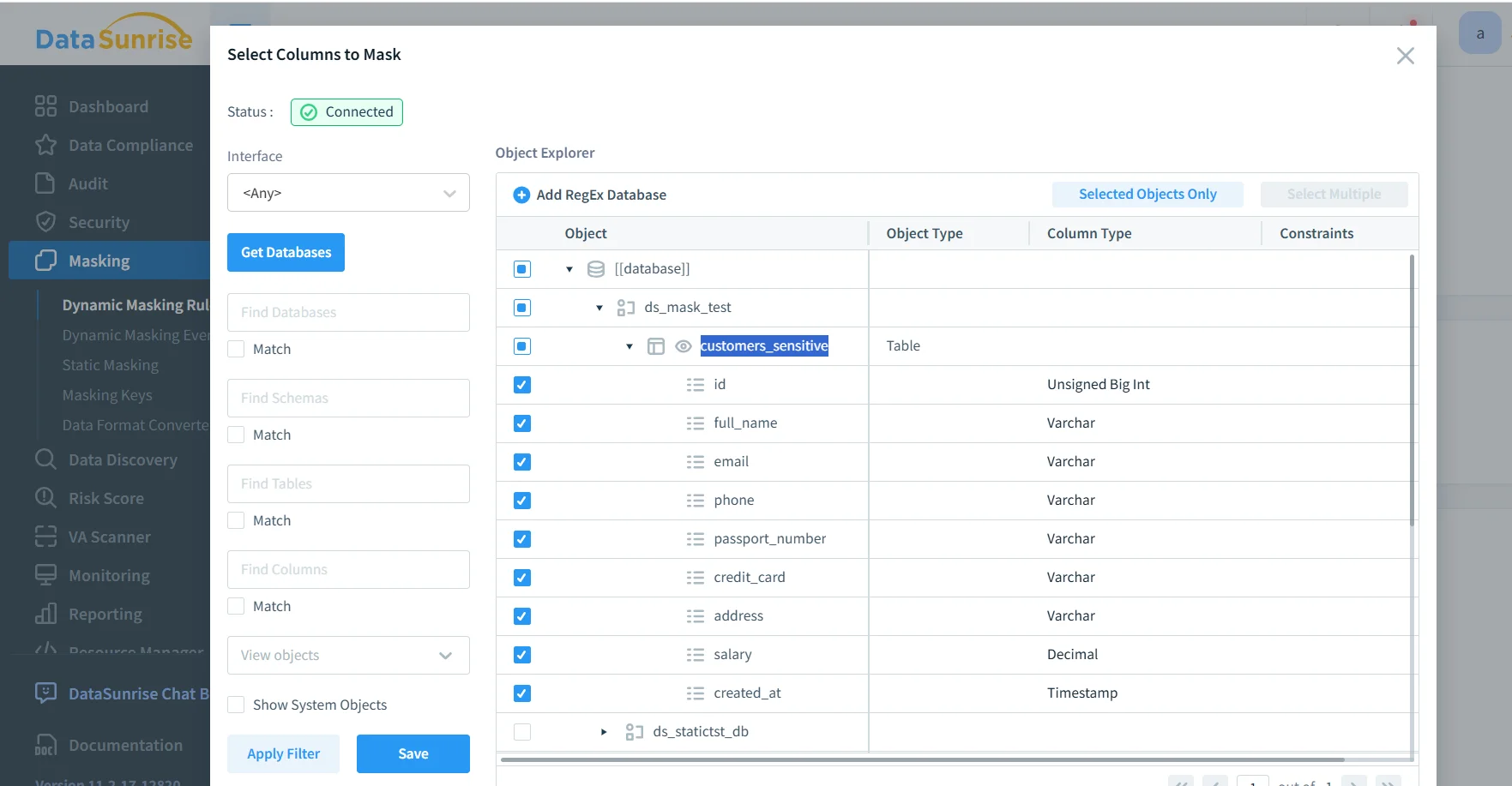
Select the MySQL table and sensitive columns that must be masked.
Choose the tables and columns that contain sensitive values. Maintain evidence using audit logs and a centralized data audit workflow. If you need full accountability, maintain structured audit trails.
3) Validate results (before and after)
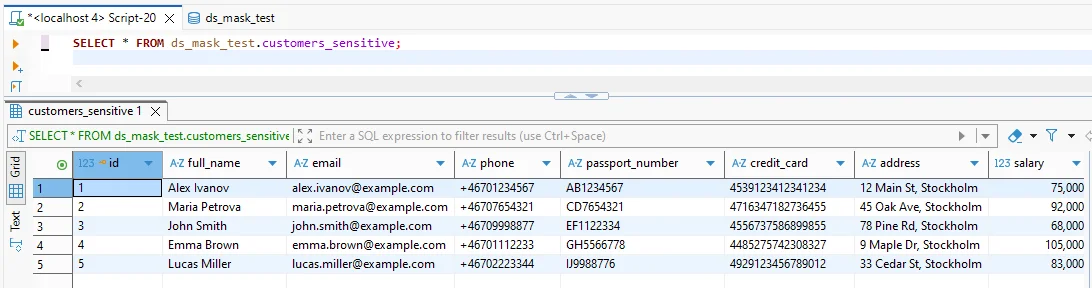
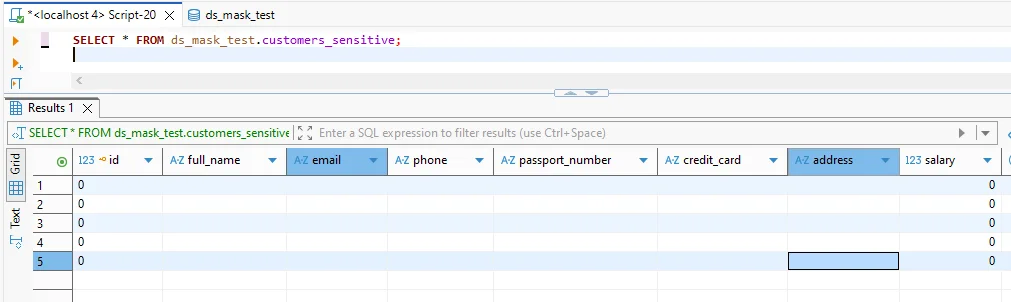
After masking: the same query returns masked output while preserving the query shape.
Test with real queries and real clients. Confirm masking doesn’t break filters, joins, or downstream processing. For ongoing visibility, enable database activity monitoring to detect suspicious access patterns.
Step 5: Combine Masking with Defense-in-Depth Controls
Masking limits exposure, but it should be part of a broader security posture:
Run vulnerability assessment to identify risky MySQL privileges, accounts, and misconfigurations.
Reduce query-based attacks using a database firewall and security rules against SQL injections.
Protect replicas and backups with database encryption and operationalize controls through continuous data protection aligned to the security guide.
Do not treat masking as your only control. If attackers gain privileged access, they can still extract sensitive data. Combine masking with least-privilege access, monitoring, encryption, and continuous auditing.
The Compliance Imperative
Regulatory requirements often determine what must be masked and what evidence must be retained:
| Regulation | MySQL Requirement | Practical Masking Approach |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Minimize personal data exposure and restrict access by purpose | Dynamic masking for non-privileged reads + auditable access controls |
| HIPAA | Protect PHI and document safeguards around access and disclosure | Mask PHI columns, monitor access patterns, and retain audit evidence |
| PCI DSS | Limit cardholder data exposure and reduce leakage risk | Mask PAN values at query time, restrict export paths, and log access |
| SOX | Maintain controlled access to financial data and reliable audit trails | Mask sensitive financial fields and maintain immutable audit records |
To keep reporting consistent across teams and platforms, many organizations use the DataSunrise Compliance Manager.
Conclusion: How to Mask Sensitive Data in MySQL Without Breaking Workflows
Masking sensitive data in MySQL works best when it is policy-driven and validated under real workloads. Discover sensitive fields, apply the right masking mode, and wrap masking with monitoring and auditing. Then harden the environment so policies can’t be bypassed.
DataSunrise supports enforcement across 40+ data platforms, so the same controls can scale beyond MySQL. To evaluate quickly, use the DataSunrise download or schedule a guided DataSunrise demo.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now