Sensitive Data Protection in Amazon OpenSearch
Sensitive data protection in Amazon OpenSearch is no longer optional. OpenSearch clusters routinely store authentication logs, customer activity traces, security telemetry, API payloads, and operational events. Those datasets frequently contain PII, identifiers, IP addresses, and other regulated information. Once indexed and searchable, that data becomes part of your compliance scope.
AWS provides the infrastructure for Amazon OpenSearch Service, but responsibility for protecting sensitive data remains with the organization operating the environment. OpenSearch does not inherently classify sensitive fields or limit what authorized users can see in results. That gap must be addressed with layered protection: discovery, masking, auditing, monitoring, and reporting.
This article outlines a practical framework for protecting sensitive data in Amazon OpenSearch using DataSunrise tools and governance controls.
Why OpenSearch Becomes a Sensitive Data Repository
OpenSearch is optimized for flexible document storage and fast retrieval. It is often fed by ingestion pipelines that prioritize speed over data minimization. As a result, sensitive information can appear in:
- Nested JSON attributes within application payloads
- Free-text “message” fields inside logs
- Support case notes or operational comments
- Authentication and authorization metadata
Even if OpenSearch is not your system of record, regulators and auditors evaluate exposure risk based on where sensitive data exists — not where it was originally generated. This is why alignment with data compliance regulations must extend to OpenSearch environments.
Core Components of Sensitive Data Protection
Protecting sensitive data in OpenSearch requires coordinated controls rather than a single feature. A practical protection model includes:
| Protection Layer | Purpose | Relevant DataSunrise Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery | Identify where sensitive fields exist | Data Discovery |
| Access Governance | Restrict visibility by role | RBAC |
| Exposure Reduction | Mask sensitive values in query results | Dynamic Data Masking |
| Monitoring | Detect unusual access patterns | Database Activity Monitoring |
| Audit & Reporting | Produce defensible evidence | Data Audit |
Step 1: Discover Sensitive Fields Before Protecting Them
Sensitive data protection starts with visibility. OpenSearch schemas evolve rapidly, and new indices may appear automatically. Manual inspection is not sustainable.
Automated data discovery identifies sensitive attributes across documents and fields, including structured and semi-structured content. Discovery results form a defensible inventory and allow you to scope governance precisely.
Without discovery, masking rules are guesswork.
Step 2: Apply Role-Based Access Controls
Sensitive data protection must align with operational roles. Not every analyst needs raw identifiers. Not every support engineer needs full personal details.
Use centralized access controls combined with least privilege principles to define who can access which indices and which level of detail they are allowed to view.
Governance policies can be managed centrally through Compliance Manager, ensuring consistent enforcement across environments.
Step 3: Enforce Dynamic Masking at Query Time
Dynamic masking protects sensitive values in real time. Instead of blocking queries entirely, masking transforms sensitive fields before they reach the user.
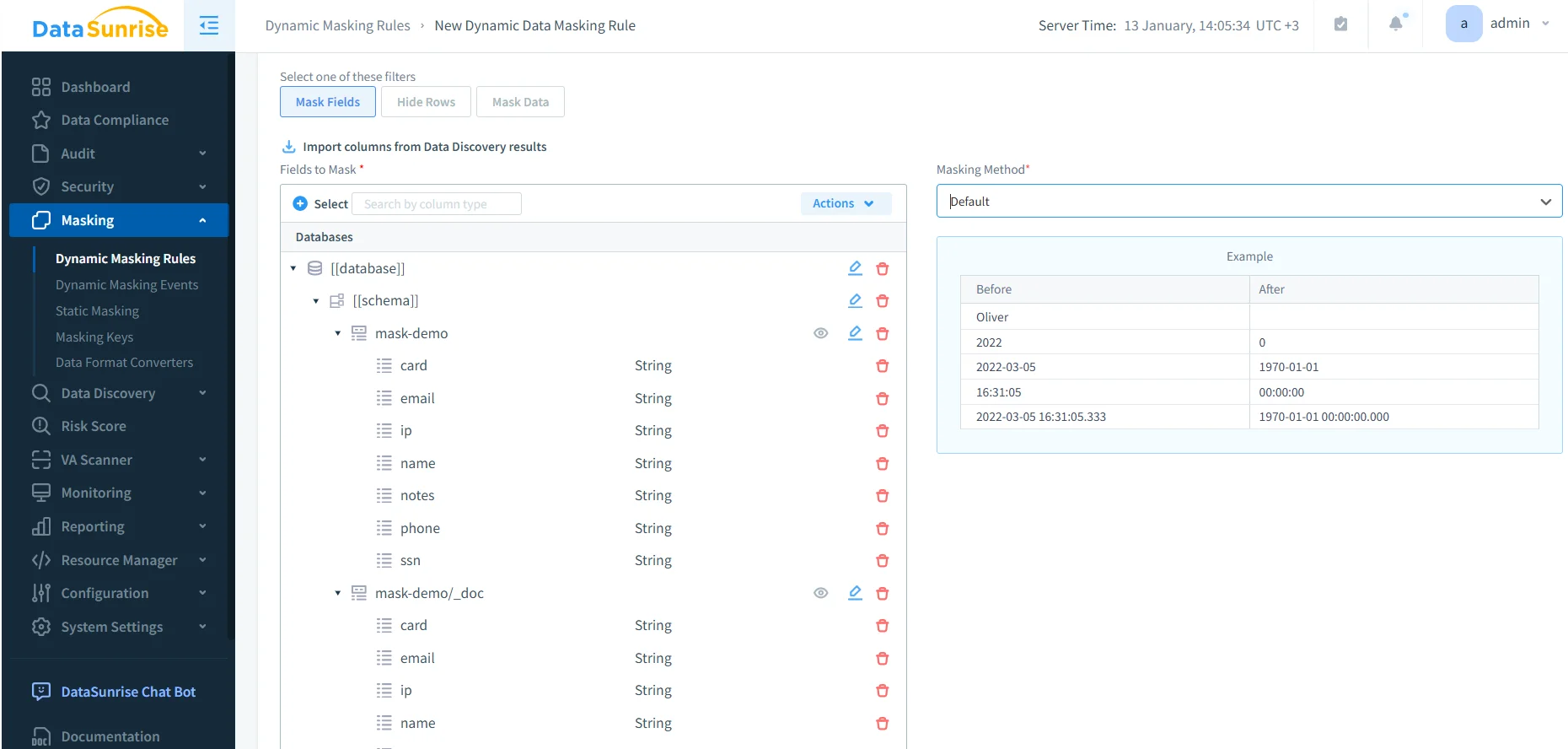
Dynamic masking techniques include:
- Full redaction for high-risk fields
- Partial masking to retain minimal operational context
- Role-based visibility differentiation
Masking outcomes should be deterministic. When multiple rules apply, resolve evaluation order using rules priority to prevent inconsistent behavior.
Step 4: Monitor Sensitive Data Access Continuously
Sensitive data protection does not stop at masking. Continuous oversight ensures policies remain effective and identifies anomalous behavior.
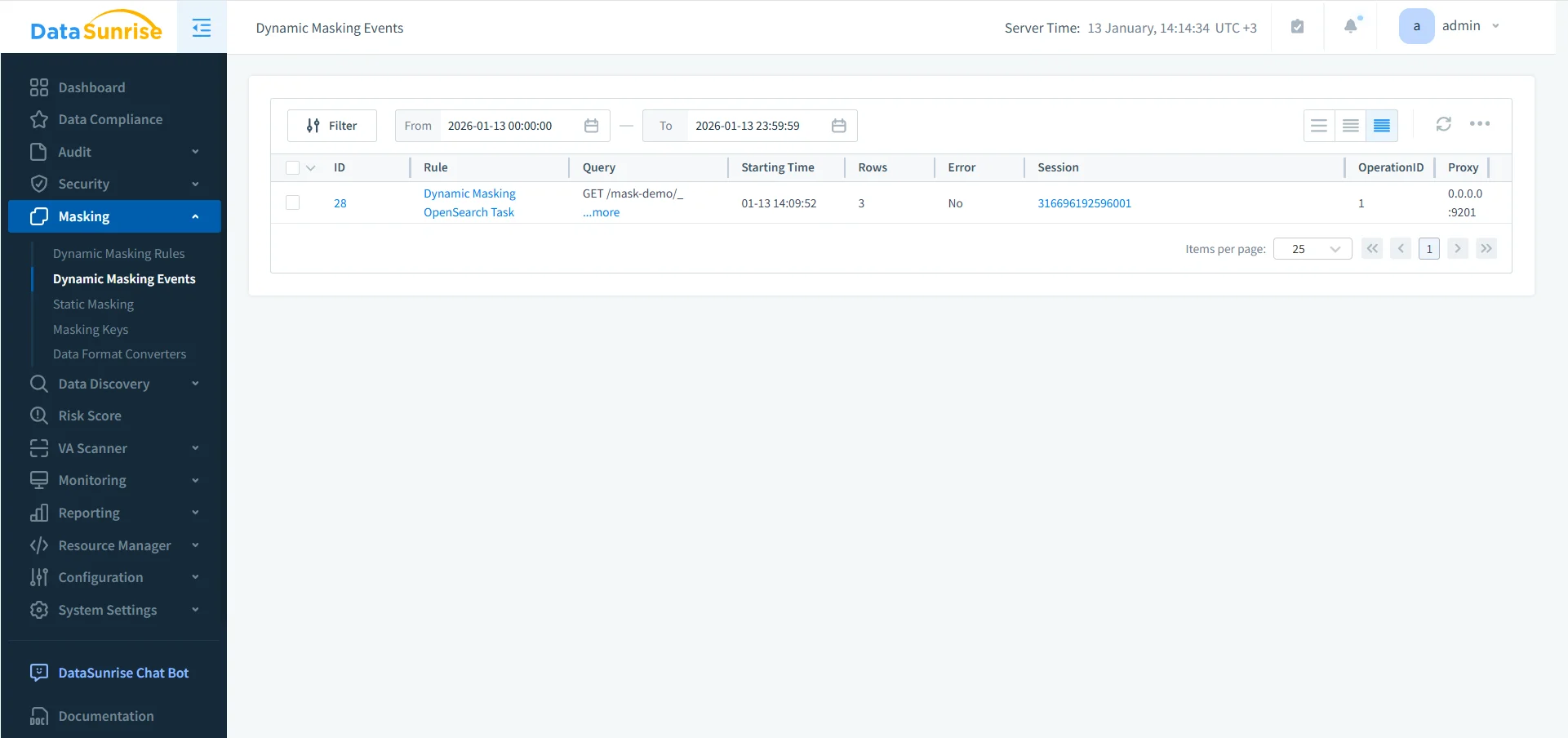
Monitoring Dynamic Masking events in DataSunrise to track enforcement activity and user sessions.
Through database activity monitoring, organizations can detect suspicious query patterns, unusual access spikes, or attempts to enumerate sensitive data.
For additional risk reduction, implement a database firewall and perform periodic vulnerability assessment to identify configuration drift and weaknesses.
Step 5: Maintain Audit-Ready Evidence
Protection controls must be provable. Regulators and auditors expect evidence of policy enforcement and access traceability.
DataSunrise centralizes evidence collection through:
AWS also provides platform-level logging reference: Amazon OpenSearch audit logs.
Centralized reporting through report generation ensures compliance reviews are structured and repeatable.
Advanced Protection Strategies
Sensitive data protection is strongest when layered. Consider supplementing masking with:
- Continuous data protection workflows
- User behavior analysis for anomaly detection
- Strict control of direct OpenSearch access paths
Each layer reduces risk independently and strengthens the overall protection model.
Start with discovery and implement dynamic masking for the highest-risk fields first. Validate results using real queries and ensure monitoring and auditing are enabled before expanding coverage.
If users can bypass the enforcement path and query OpenSearch directly, masking controls are ineffective. Lock down network paths, enforce centralized access, and keep auditing continuously enabled.
Conclusion
Sensitive data protection in Amazon OpenSearch requires coordinated governance, not isolated controls. By combining discovery, role-based access management, dynamic masking, monitoring, and centralized auditing, organizations can reduce exposure without disrupting search-driven operations.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now