
What is Database Audit?
Most data breaches do not begin with sophisticated or highly technical attacks. More often, they originate from routine operational mistakes: an account that remains active longer than it should, a contractor granted excessive privileges, or sensitive information transmitted through an unsecured channel. Each of these actions leaves a trace. Data auditing gathers these traces and organizes them into a structured record that shows what happened, who performed the action, when it occurred, and under which conditions. For security and compliance teams, this record provides clear, verifiable evidence instead of assumptions.
When auditing is combined with advanced analytics and automated alerting, it shifts from being purely investigative to becoming a preventive security capability. Organizations can detect abnormal behavior earlier, enforce least-privilege access more consistently, and verify that data usage follows both internal policies and regulatory obligations. Solutions such as User Behavior Analysis (UBA) strengthen this process by identifying unusual user activity patterns in real time.
- Identifying brute-force attacks and port scanning activities
- Preventing organization-wide malware and virus spread
- Discovering unauthorized software on workstation networks
- Countering internet-based fraud and phishing schemes
- Analyzing operational system failures and outages
- Detecting software vulnerabilities and performance issues
- Finding security gaps in data storage and access controls
Example: An employee with outdated access credentials downloads sensitive HR data after moving to a new department. Without audit logging in place, the activity goes unnoticed for weeks. With DataSunrise, this event would trigger a real-time alert and be logged with full session context for investigation.
Traditional security efforts focus on external threats. However, internal risks from employees or contractors often go undetected. Data leaks through messaging platforms, cloud sync, or social media bypass conventional DLP tools. In many cases, users unintentionally expose sensitive information simply by exporting reports to personal devices, syncing database snapshots through consumer cloud apps, or sharing screenshots containing confidential records. These subtle behaviors are rarely caught by perimeter security controls.
Standard DLP solutions monitor file transfers and email communications. But databases hold the most sensitive information. They use specialized protocols that traditional DLP tools cannot parse. As a result, unauthorized queries, privilege abuse, and mass data extraction via SQL traffic remain invisible to traditional monitoring solutions. This is why organizations need database-specific security with comprehensive audit capabilities. Purpose-built monitoring captures query-level actions, correlates user identities, and detects anomalous access patterns—providing visibility and control that general-purpose DLP systems cannot deliver.
Key Takeaways: Database Auditing
- Database auditing extends DLP coverage by analyzing SQL activity and user behavior directly at the data layer.
- Focus audit logs on your most critical schemas to reduce overhead and improve threat visibility.
- Forward structured audit trails to your SIEM for better correlation and real-time threat detection.
- Use DataSunrise Database Audit to enforce consistent policies across Oracle, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and cloud databases.
Building Database Audit Foundations
PostgreSQL Trigger: Establishing Basic Logging
Development teams can implement basic database logging with PostgreSQL triggers. This approach captures INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations. It provides a practical foundation for comprehensive audit workflows:
-- PostgreSQL: Comprehensive audit trail for data operations
CREATE TABLE audit_log (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
operation TEXT NOT NULL,
user_name TEXT NOT NULL,
table_name TEXT NOT NULL,
old_row JSONB,
new_row JSONB,
executed_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT current_timestamp,
session_id TEXT,
client_ip INET
);
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION audit_trigger_fn()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN
INSERT INTO audit_log(operation, user_name, table_name, old_row, new_row, session_id, client_ip)
VALUES (
TG_OP,
session_user,
TG_TABLE_NAME,
CASE WHEN TG_OP = 'DELETE' THEN row_to_json(OLD) ELSE NULL END,
CASE WHEN TG_OP = 'INSERT' THEN row_to_json(NEW) ELSE row_to_json(NEW) END,
current_setting('application_name', true),
inet_client_addr()
);
IF TG_OP = 'DELETE' THEN
RETURN OLD;
ELSE
RETURN NEW;
END IF;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql SECURITY DEFINER;
-- Apply trigger to sensitive tables
CREATE TRIGGER audit_trigger
AFTER INSERT OR UPDATE OR DELETE ON employees
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION audit_trigger_fn();
This script works well for development environments or smaller deployments. For enterprise-scale compliance and advanced controls, organizations use specialized platforms like DataSunrise.
Heads-up Full-fidelity logging on a 5 TB OLTP cluster can add ≈30 % I/O and 150 GB/day of storage. Scope audits to high-risk schemas or budget accordingly.
Database Auditing — TL;DR, Checklist, Fixes
TL;DR (60 seconds)
- Enable native audit (
pgAudit/ SQL Server Audit / MySQL Audit). - Normalize events: actor, role, object, action, status, sensitivity.
- Tag PII/PHI/PCI at ingestion; alert on off-hours reads & bulk SELECT.
- Ship to SIEM; correlate with Activity Monitoring.
- Make evidence tamper-evident (hash chain or WORM/immutable store).
Implementation Checklist (8 steps)
- Scope high-risk schemas/roles and include failed attempts.
- Enable audit with minimal noise (
read,write,ddl). - Adopt a standard event schema (actor, role, object, action, status, tags).
- Apply sensitivity tags (PII/PHI/PCI) at ingestion.
- Create alerts: bulk reads, role change → DDL, dormant account login.
- Forward to SIEM and correlate with DataSunrise.
- Enforce rotation, retention, integrity (hash/WORM).
- Publish auditor-ready reports (SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS).
Native vs. DataSunrise — 10-second call
| Use Case | Native Only | DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Single DB, lightweight evidence | ✔️ | — |
| Multi-DB estate, one console | — | ✔️ |
| Real-time alerts & behavior analytics | Limited | ✔️ |
| Compliance packs & exports | DIY | Pre-built |
| Immutable, normalized trails | Manual | Built-in options |
Rule of thumb: combine when you want DB-local logs + centralized correlation; replace when you manage many engines and need one pane of glass.
Enterprise Database Security and Monitoring
Real-Time Monitoring with DataSunrise
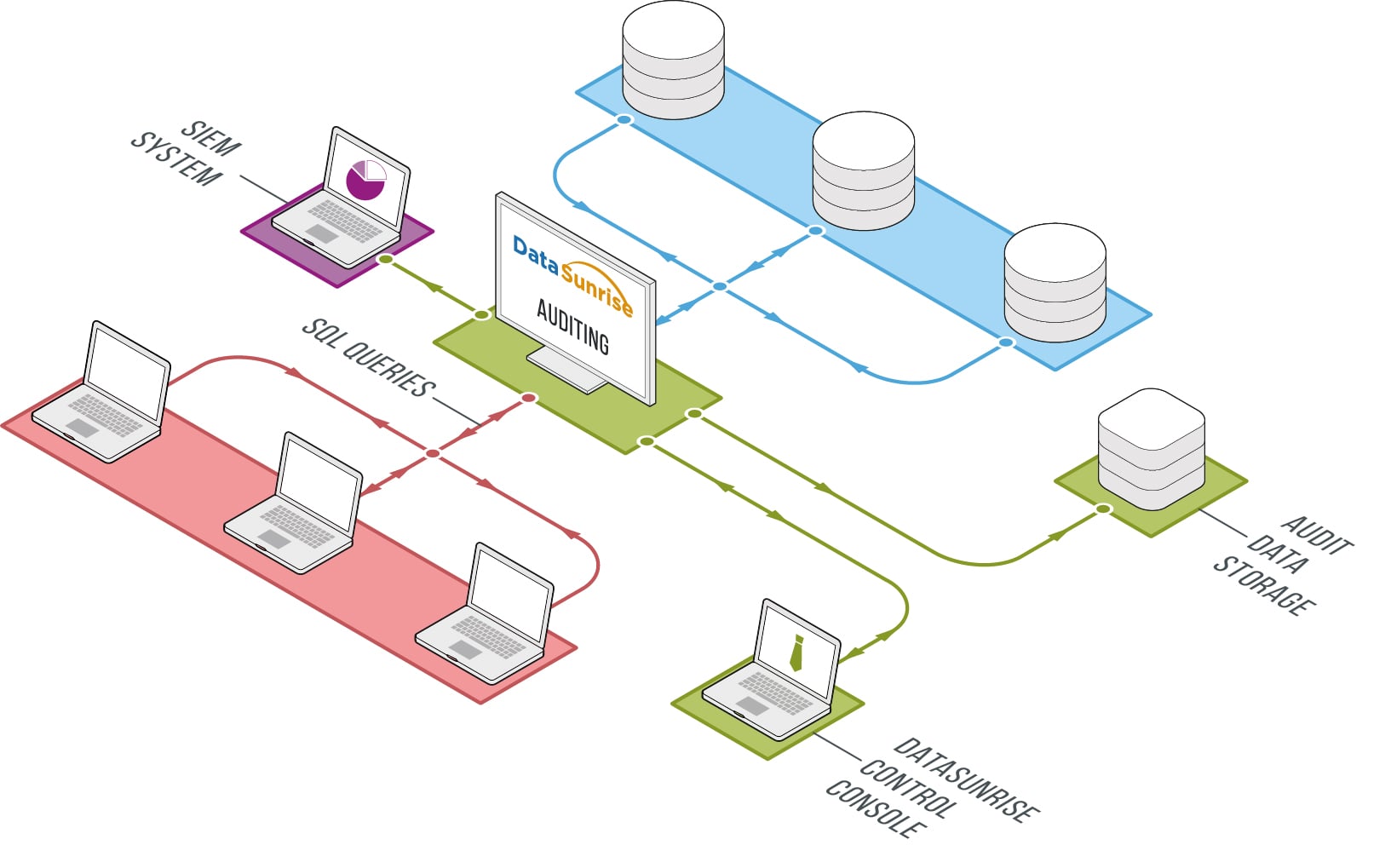
DataSunrise Security Suite provides deep packet inspection across database platforms. Its activity monitoring engine captures user behavior patterns. Audit logs export to SIEM systems through Syslog for real-time correlation and alerting.
Tip: Pair database activity monitoring with advanced audit logging to reduce detection times and strengthen compliance posture across hybrid environments.
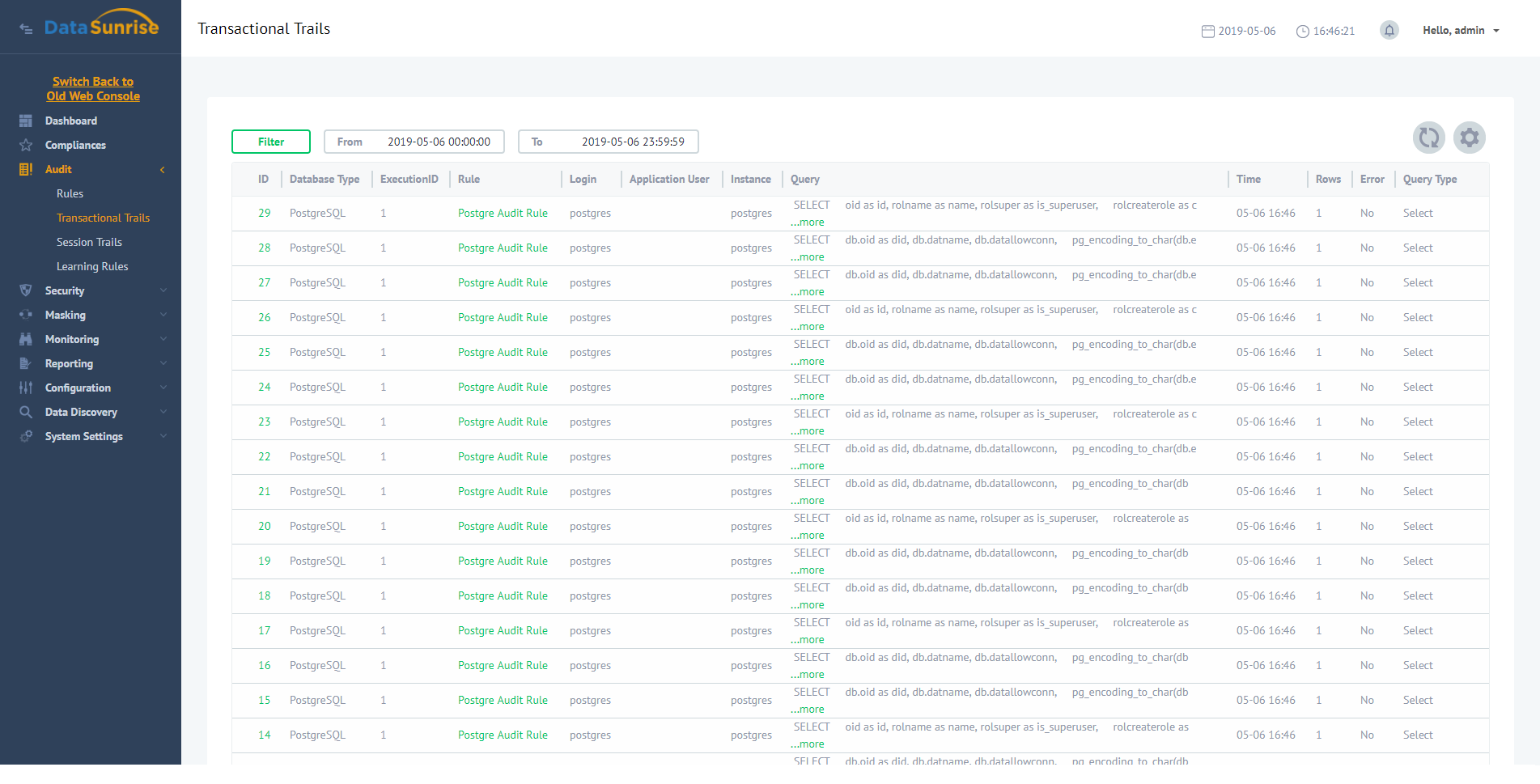
Beyond breach detection, audit logs help determine incident scope. Unusual query patterns, access spikes, or privilege abuse get flagged and traced. The Database Audit module uses pattern recognition to identify anomalies. It classifies them for detailed analysis.
Regulatory Compliance Through Audit Logging
SOX Compliance Through Audit Management
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires precise auditing of data access and privilege changes in financial systems. DataSunrise addresses these requirements by capturing:
- 1.1 Events from privileged users and unauthorized access attempts
- 1.2 Role escalations and access level changes
- 1.3 Failed authentication attempts and access denials
The System Events module logs authentication attempts and configuration changes. It helps identify unauthorized privilege use or system misconfigurations.
- 1.4 Database schema changes and data definition modifications
- 1.5 Unauthorized attempts to access protected financial data
Each audit entry includes session details and executed SQL statements. It captures IP addresses, user IDs, and affected tables. This enables compliance teams to track changes with exceptional precision.
PCI DSS Logging and Compliance
PCI DSS requires continuous audit logging for systems processing cardholder data. DataSunrise streamlines compliance with customizable rules and secure log storage.
- 10.1 Link each database operation to authenticated users
Sessions are monitored from login through logout. All queries and accessed objects get recorded comprehensively.
- 10.2 Automatically record access to sensitive tables and fields
- 10.3 Attach timestamps, usernames, source IPs, and result status
DataSunrise audit logs meet PCI format standards. They export in CSV and PDF formats. Optional data discovery adds classification for card numbers and PII.
- 10.5 Ensure logs are securely stored and protected from tampering
Logs write to PostgreSQL, MySQL, or SQLite databases. They can offload to external servers or SIEM tools for backup and retention.
- 10.6 Continuously monitor for suspicious activity in audit records
Each security rule can trigger real-time alerts. This gives security teams opportunities to respond before damage occurs.
Important Note: Additional PCI subclauses may require organization-specific configurations beyond this overview.
| Audit Event | ATT&CK ID | Detection Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk SELECT on PII | T1030 | affected_rows > 10 000 |
| Schema change outside change window | T1070.006 | ddl_change & !business_hours |
| Dormant account login | T1078 | last_seen > 90 days |
Native Audit Cheatsheet (SQL Server & MySQL)
If you’re still running native-only, here are minimal, production-ready snippets to capture database activity history without third-party tooling.
SQL Server: Audit to File + Quick Read
-- Create a server audit writing to disk
CREATE SERVER AUDIT Audit_File
TO FILE (FILEPATH = 'C:\SQLAudits\', MAXSIZE = 1 GB, MAX_ROLLOVER_FILES = 20)
WITH (QUEUE_DELAY = 1000, ON_FAILURE = CONTINUE);
ALTER SERVER AUDIT Audit_File WITH (STATE = ON);
-- Track SELECT/WRITE on a critical DB (replace MyDB)
CREATE DATABASE AUDIT SPECIFICATION DbSpec_MyDB
FOR SERVER AUDIT Audit_File
ADD (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON DATABASE::MyDB BY PUBLIC),
ADD (SCHEMA_OBJECT_CHANGE_GROUP)
WITH (STATE = ON);
-- Read last hour of events
SELECT event_time, server_principal_name, database_name, statement
FROM sys.fn_get_audit_file('C:\SQLAudits\*.sqlaudit', DEFAULT, DEFAULT)
WHERE event_time > DATEADD(HOUR, -1, GETDATE())
ORDER BY event_time DESC;MySQL 8: Enterprise Audit (JSON)
-- Enable the audit plugin (paths vary by distro)
INSTALL PLUGIN audit_log SONAME 'audit_log.so';
-- JSON format; log everything but you should scope in prod
SET PERSIST audit_log_format = JSON;
SET PERSIST audit_log_policy = ALL;
-- Optional: rotate & size controls
SET PERSIST audit_log_rotate_on_size = 104857600; -- 100 MB
SET PERSIST audit_log_file = 'audit.log';
-- Example: verify plugin status
SHOW PLUGINS LIKE 'audit%';Native audit works—but every engine has different knobs, file formats, and blind spots. Correlation becomes a full-time job.
Tamper-Evident Audit Store (PostgreSQL Hash Chain)
Compliance loves immutability. This pattern writes a hash chain over your audit events so any tampering is obvious. Pair it with WORM storage (e.g., S3 Object Lock) for the belt-and-suspenders approach.
-- Requirements: pgcrypto
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pgcrypto;
-- Append-only audit table
CREATE TABLE audit_events (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
event_time TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL DEFAULT now(),
actor TEXT NOT NULL,
action TEXT NOT NULL,
object TEXT,
ip INET,
payload JSONB,
prev_hash BYTEA, -- previous row hash
row_hash BYTEA -- current row hash
);
-- Prevent updates/deletes
ALTER TABLE audit_events
ALTER COLUMN actor SET NOT NULL,
ALTER COLUMN action SET NOT NULL;
REVOKE UPDATE, DELETE ON audit_events FROM PUBLIC;
-- Insert wrapper to compute the hash chain
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION audit_events_append()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
DECLARE
v_prev BYTEA;
BEGIN
SELECT row_hash INTO v_prev
FROM audit_events
ORDER BY id DESC
LIMIT 1;
NEW.prev_hash := v_prev;
NEW.row_hash := digest(
coalesce(NEW.actor,'') || '|' ||
coalesce(NEW.action,'') || '|' ||
coalesce(NEW.object,'') || '|' ||
coalesce(NEW.ip::text,'') || '|' ||
coalesce(NEW.payload::text,'') || '|' ||
coalesce(NEW.event_time::text,'') || '|' ||
encode(coalesce(NEW.prev_hash, '\\x'), 'hex'),
'sha256');
RETURN NEW;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
CREATE TRIGGER trg_audit_chain
BEFORE INSERT ON audit_events
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION audit_events_append();
-- Verification query: detect breaks in the chain
WITH ordered AS (
SELECT id, row_hash, prev_hash,
lag(row_hash) OVER (ORDER BY id) AS expected_prev
FROM audit_events
)
SELECT *
FROM ordered
WHERE prev_hash IS DISTINCT FROM expected_prev;Result set must be empty. Any row returned indicates tampering or a broken chain.
Key Components of a Modern Data Audit Architecture
To implement effective database audit strategies, teams must design secure, scalable architectures that support real-time monitoring, structured logging, and automated compliance reporting. Below are essential components found in high-performing audit systems:
- Audit Capture Layer: Intercepts SQL queries, data definition changes, and user logins without affecting application performance. Tools like DataSunrise act as transparent proxies across Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, and more.
- Log Normalization Engine: Converts raw audit events into a structured schema with consistent metadata—username, IP, timestamp, session ID, object accessed—regardless of database engine.
- Secure Audit Store: Retains logs in tamper-proof, immutable formats. Options include append-only PostgreSQL tables, external S3 buckets, or hardened SIEM integrations.
- Alerting and Correlation: Detects anomalies through rule-based or ML-powered models. For example, repeated access to PII by dormant accounts triggers escalation workflows.
- Reporting and Evidence Layer: Generates audit-ready reports in PDF, CSV, or custom JSON formats. Supports regulatory audits for SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
These components enable organizations to detect breaches early, enforce least-privilege principles, and produce defensible logs during investigations. A modern data audit architecture doesn’t just record—it responds, correlates, and proves compliance.
Data Audit Requirements Across Regulations
Audit logging is a cornerstone of modern compliance. Each framework emphasizes traceability and accountability in slightly different ways. Mapping your data audit practices to these frameworks ensures readiness for external reviews and reduces compliance risk:
| Framework | Audit Expectations | How DataSunrise Helps |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Log personal data access, prove lawful basis for processing, and detect misuse quickly. | Granular audit policies for PII with automated reports for regulators. |
| HIPAA | Maintain full trails of PHI access, modifications, and disclosure attempts. | Centralized, tamper-evident logging with PHI tagging and integrity checks. |
| PCI DSS | Track cardholder data usage, failed login attempts, and suspicious queries. | Real-time monitoring with rule-based alerts for sensitive payment data. |
| SOX | Ensure accountability for financial record changes and privileged user actions. | Detailed trails of schema changes and access escalations with auditor-ready exports. |
By aligning audit logs with regulatory frameworks, DataSunrise Database Audit transforms raw database traces into compliance evidence, reducing manual preparation and improving security posture.
Measuring Data Audit Effectiveness
- MTTD: Detect suspicious activity in under 5 minutes
- Coverage: ≥95% of sensitive objects continuously monitored
- False Positive Rate: <1% with refined rules and tagging
- Compliance Readiness: Audit evidence available on demand
- Storage Efficiency: Log rotation and compression save 40–60% space
Industry Use Cases
Effective data auditing supports:
- Finance: Trace privilege abuse and insider fraud
- Healthcare: Prove PHI access accountability for HIPAA
- SaaS: Deliver audit evidence to customers for trust and compliance
- Government: Strengthen oversight and transparency
Data Audit FAQ
What is data auditing?
Data auditing is the systematic collection and review of database events—queries, logins, privilege changes, and schema updates—to establish accountability, support investigations, and demonstrate compliance.
How does database auditing differ from traditional DLP?
Traditional DLP inspects files and network traffic. Database auditing observes SQL activity at the data layer, linking actions to authenticated identities and specific objects, which improves traceability and evidence quality.
Which regulations rely on database audit evidence?
Regulatory frameworks such as SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require or strongly recommend audit logging to establish access transparency and control effectiveness.
How do I limit performance impact?
- Prioritize sensitive schemas and high-risk actions.
- Stream events to SIEM or a proxy to offload processing.
- Apply rotation, compression, and retention policies.
- Review noise routinely and refine rules.
What metrics show an effective audit program?
- Coverage of sensitive objects monitored.
- Mean time to detect (MTTD) and respond (MTTR).
- Alert precision (true/false positive ratio).
- Log integrity verification rate.
- Storage growth vs. retention objectives.
When should we move beyond native tools?
Scale, multi-DB estates, and compliance reporting needs typically warrant a platform with centralized policies, normalization, real-time alerting, and reporting. See DataSunrise Database Audit and Activity Monitoring.
The Future of Data Auditing
As threats evolve and compliance standards tighten, data auditing is shifting beyond simple log collection. Emerging trends include:
- AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: Machine learning models highlight deviations in SQL activity that human analysts might miss.
- Zero-Trust Enforcement: Every query is verified against contextual policies, reducing reliance on perimeter security.
- Immutable Audit Records: Blockchain and hash-chained storage provide tamper-proof evidence for regulators.
- Cloud-Native Integration: Direct pipelines to SIEM, SOAR, and CSPM platforms for unified security operations.
Organizations adopting these strategies move from reactive logging to proactive defense, ensuring data audit practices remain both compliant and resilient.
Conclusion: Advancing Data Audit and Governance Controls
DataSunrise brings together automated enforcement, live activity monitoring, and compliance-focused audit logging within a unified auditing framework. Rather than relying on manual supervision, security and compliance teams gain continuous visibility into every query, configuration change, and access attempt across their database environments. Each recorded action includes detailed contextual metadata such as user identity, source IP, application context, and executed SQL statements. This level of traceability improves accountability and allows investigators to reconstruct activity timelines during incident analysis.
In addition to basic logging, the platform supports rule-based auditing policies that help organizations monitor specific objects, schemas, users, or types of queries. Security teams can configure alerts, automated responses, and centralized reporting dashboards to quickly identify suspicious patterns or policy violations. As a result, organizations can move from reactive investigations to proactive monitoring, enabling faster detection of anomalies and stronger enforcement of governance standards.
Designed for heterogeneous environments, DataSunrise integrates with major database systems including Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Amazon Redshift, PostgreSQL, and MySQL. The platform supports both on-premises installations and cloud-native deployments, making it well-suited for hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. Teams can evaluate the solution through local installations or launch it directly via the AWS Marketplace and Microsoft Azure Marketplace. This deployment flexibility accelerates onboarding while minimizing disruption to existing infrastructure and compliance workflows.
By centering on policy-driven, automated auditing, DataSunrise enables organizations to maintain regulatory alignment, reduce investigation timelines, and generate defensible audit evidence for internal and external reviews. Audit records evolve from passive logs into actionable security intelligence that strengthens risk management and governance strategies. As compliance obligations grow and data infrastructures expand, DataSunrise helps organizations maintain consistent oversight, operational resilience, and long-term security maturity.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now