Databricks SQL Data Audit Trail
Databricks SQL has become a central analytics engine for organizations adopting lakehouse architectures. It enables business intelligence, reporting, and ad-hoc analytics directly on cloud storage while supporting large numbers of users and automated workloads. As data volumes and access patterns grow, maintaining a reliable Databricks SQL audit trail becomes essential for understanding how data is accessed, modified, and shared across the platform.
In modern analytical environments, data access is rarely static. Analysts explore datasets interactively, BI tools issue scheduled queries, and applications generate automated workloads. Because these access patterns overlap, organizations need an audit trail that captures data interactions consistently across users, tools, and execution contexts. This requirement closely aligns with the principles of data management and controlled data accessibility.
A data audit trail focuses specifically on interactions with data objects rather than infrastructure events. It records how tables, schemas, and columns are queried or changed over time. In distributed Databricks SQL environments, where multiple users, BI tools, and applications operate concurrently, a structured audit trail provides the foundation for security investigations, governance, and regulatory compliance.
This article explains what a Databricks SQL audit trail is, why native logging is often insufficient, and how DataSunrise enables centralized, data-centric audit trails using real-time monitoring, transactional history, and policy-driven controls.
What Is an Audit Trail in Databricks SQL?
A Databricks SQL audit trail is a chronological record of actions that affect data objects. It captures which datasets were accessed, which SQL statements were executed, and how those operations impacted tables and schemas. Unlike simple query logs, an audit trail preserves context and execution order, forming a true database activity history.
More importantly, an audit trail connects individual events into a coherent sequence. Rather than treating each query as an isolated record, it links activity back to a specific session, user, or application workflow. This linkage is critical for effective database activity monitoring.
For example, a complete audit trail links a SELECT statement to the session and user that initiated it, then connects subsequent UPDATE or DELETE operations to the same workflow. This continuity allows teams to reconstruct exactly how data was accessed or modified during a given time period.
Such traceability is critical for organizations operating under regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. Regulators expect organizations to prove not only that logging exists, but also that data access can be reconstructed and explained in a defensible way.
Why Native Databricks Logs Are Not Enough
Databricks provides native audit logs that capture workspace-level and SQL execution events. These logs typically include query text, timestamps, user identities, and high-level operation types. Teams often export this telemetry to external platforms such as Azure Log Analytics, Amazon CloudWatch, or Google Cloud Logging.
While native logs are useful for operational troubleshooting, they were not designed to function as a complete data-level audit trail. Correlating events across sessions, users, and data objects often requires manual processing or custom scripts, which introduces risk and delays.
In addition, native logs focus on execution events rather than data impact. They do not always provide clear insight into which tables or schemas were affected, especially when complex joins, views, or nested queries are involved. For organizations that need defensible audit evidence, these limitations create gaps in data security and database security.
Connecting Databricks SQL for Audit Trail Collection
To build a reliable audit trail for Databricks SQL, an auditing system must establish a secure and continuous connection to the warehouse. This connection allows the system to observe SQL activity in real time without interfering with query execution or performance.
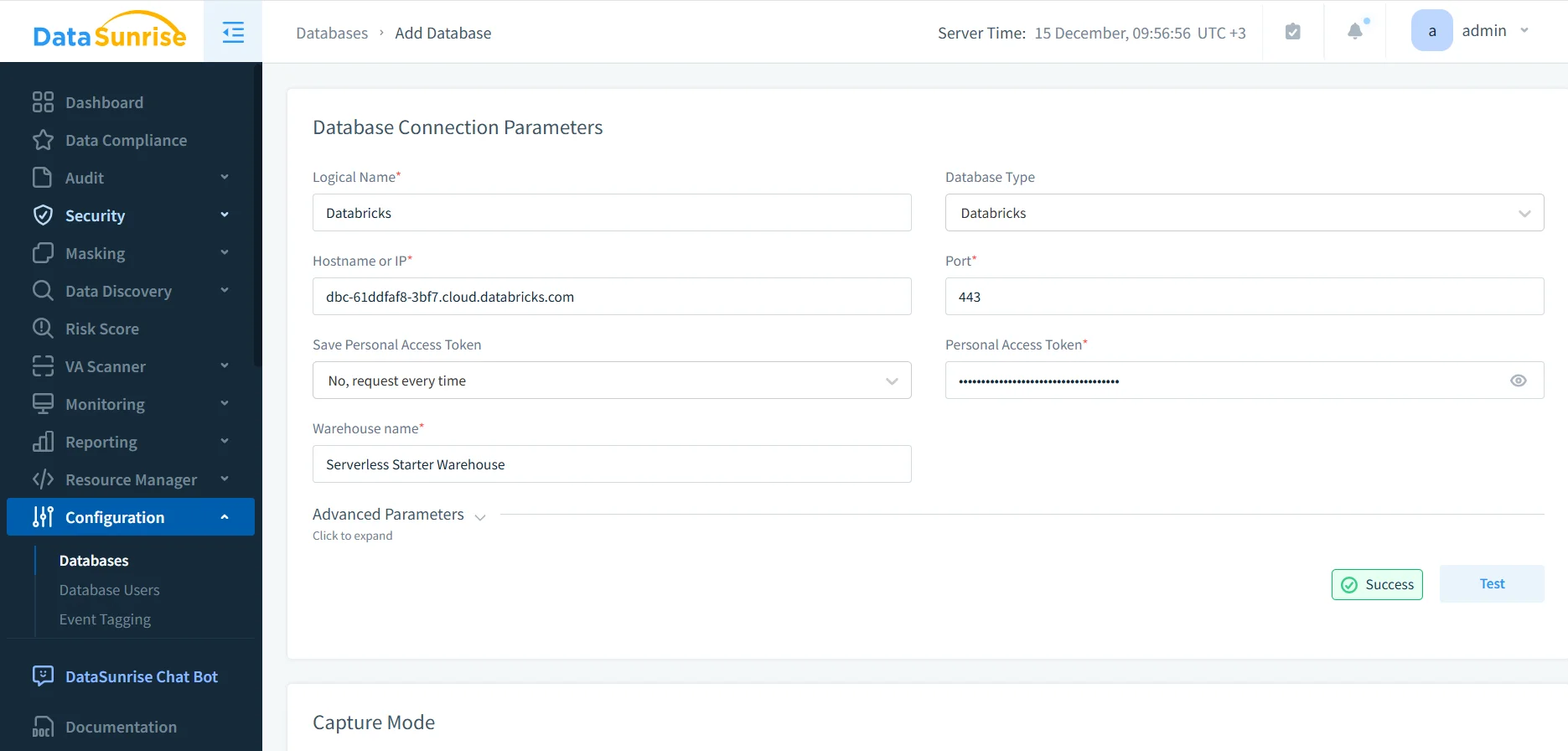
During configuration, administrators define parameters such as hostname, port, warehouse name, and authentication method. Once the connection is active, the auditing layer can begin capturing SQL activity related to data access and modification. This deployment model is consistent with DataSunrise’s deployment modes and proxy-based architecture.
Selecting Data Objects for Auditing
Effective auditing does not require monitoring every object in the environment. Instead, organizations typically focus on schemas and tables that contain sensitive, regulated, or business-critical data discovered through data discovery processes.
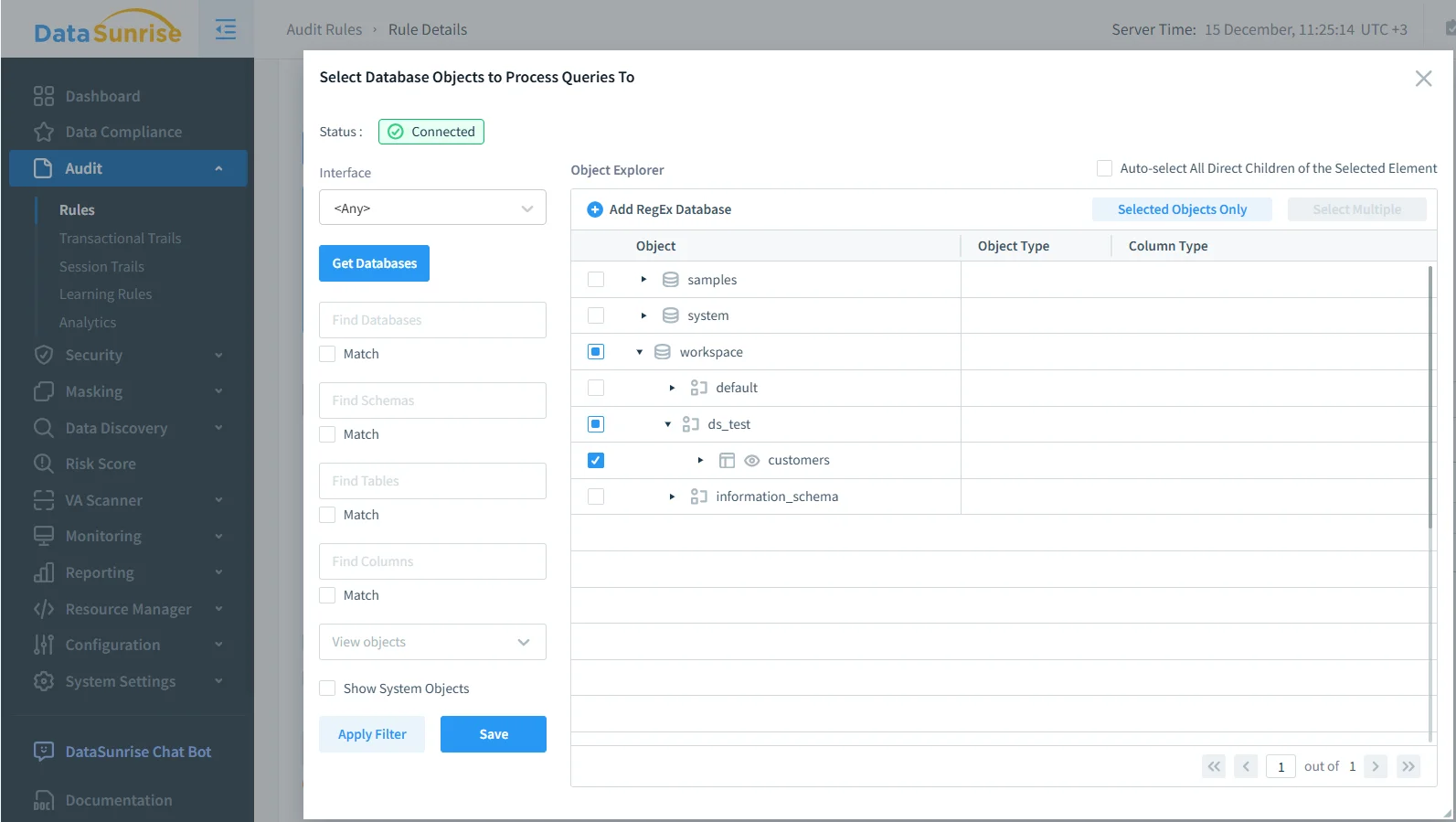
By targeting specific objects, teams reduce noise and create an audit trail that highlights meaningful data access events. This selective approach also improves performance and supports the principle of least privilege.
Transactional Audit Trails for Databricks SQL
Once audit rules are active, DataSunrise records events in a transactional audit trail. This trail preserves the exact order in which SQL operations occur, creating a reliable timeline of data access and modification suitable for forensic analysis.
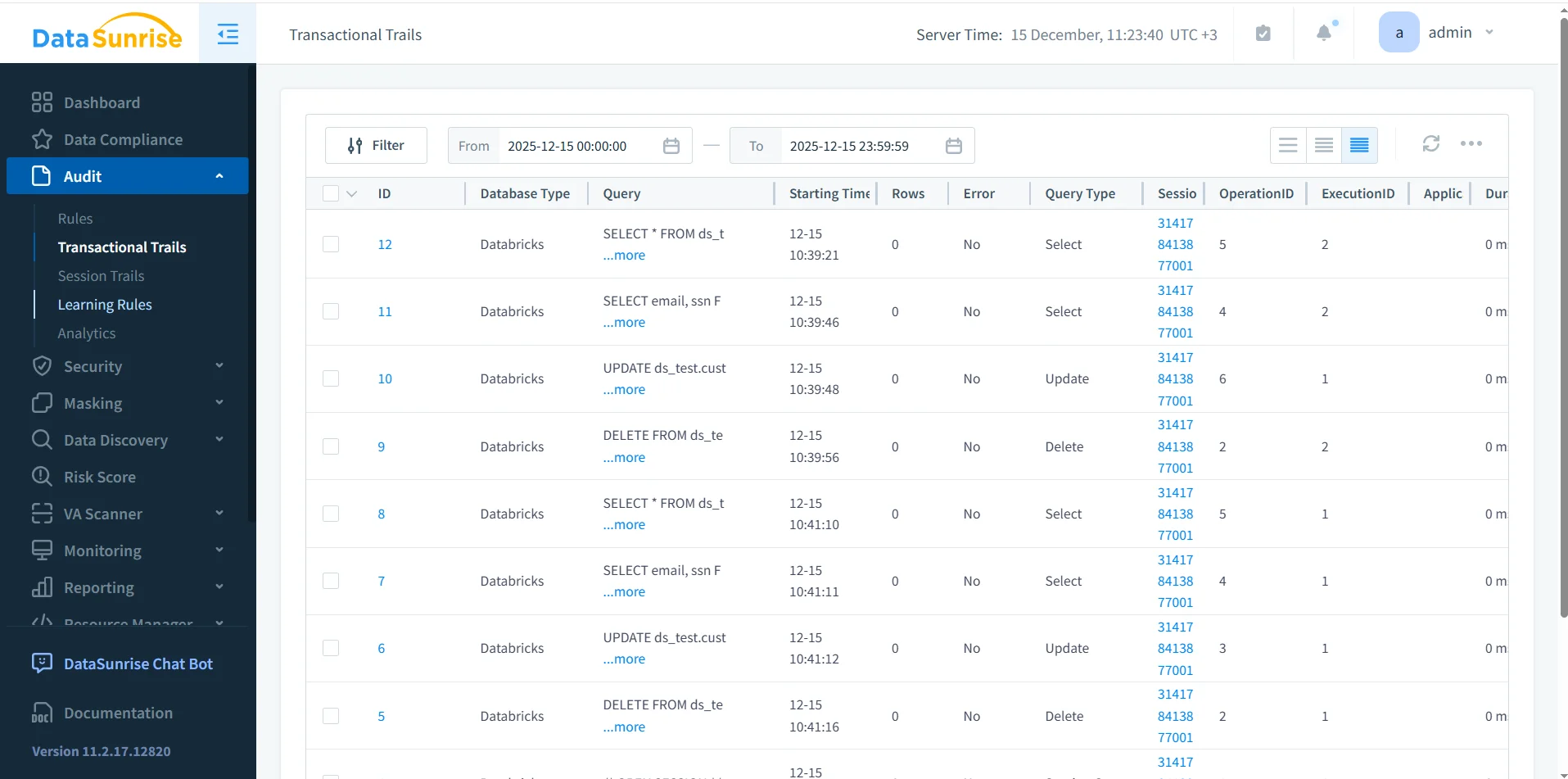
Each audit entry includes query text, execution time, query type, session identifiers, and execution status. Together, these attributes allow teams to reconstruct how specific datasets were accessed and modified, which is essential for user behavior analysis and incident response.
This transactional view supports forensic analysis and compliance reporting. It also aligns with established practices described in audit logs and audit trail methodologies.
Conclusion: Building a Databricks SQL Audit Trail
Databricks SQL delivers powerful analytics, yet data-driven environments demand more than basic logging. A reliable audit trail must preserve context, execution order, and object-level visibility while integrating with broader governance controls.
A Databricks SQL audit trail built with DataSunrise captures real-time activity, tracks access to critical datasets, and produces structured audit evidence for investigations, compliance audits, and ongoing data audit programs.
With a well-defined audit trail in place, organizations can confidently scale Databricks SQL while maintaining transparency, control, and regulatory alignment.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now