Amazon DynamoDB Audit Log
Amazon DynamoDB delivers low-latency data access at scale, but that convenience hides an uncomfortable truth: without a reliable audit log, you have no visibility into who modified what, when, or why. For regulated workloads, an audit log is not optional — it’s the backbone of evidence, traceability, and accountability. DynamoDB itself offers powerful operational capabilities, documented in the official DynamoDB Developer Guide, but effective auditing requires understanding how its surrounding AWS services generate and manage log data.
This page explains how DynamoDB generates audit logs natively, the limitations of AWS-only mechanisms, and how DataSunrise enhances audit visibility with real-time monitoring, rule-based tracking, and compliance alignment.
Importance of Audit Log
In DynamoDB environments, an audit log is more than a historical record — it is a security control, compliance mechanism, and operational safeguard. Audit logs reveal how data is accessed, modified, and distributed across applications and microservices. They support investigations by identifying who performed an operation, from where, and under which credentials. They also expose insider misuse, flawed automation, or configuration drift.
Audit logs are essential for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. A deeper explanation of core audit mechanisms is available in Audit Trails.
Organizations operating multi-cloud or hybrid data environments often rely on Data Audit to consolidate audit events across platforms.
How DynamoDB Produces Audit Logs
DynamoDB does not store audit trails inside its tables. Instead, it relies on AWS services that capture operational, access, and data-level events. A related overview can be found in Database Audit.
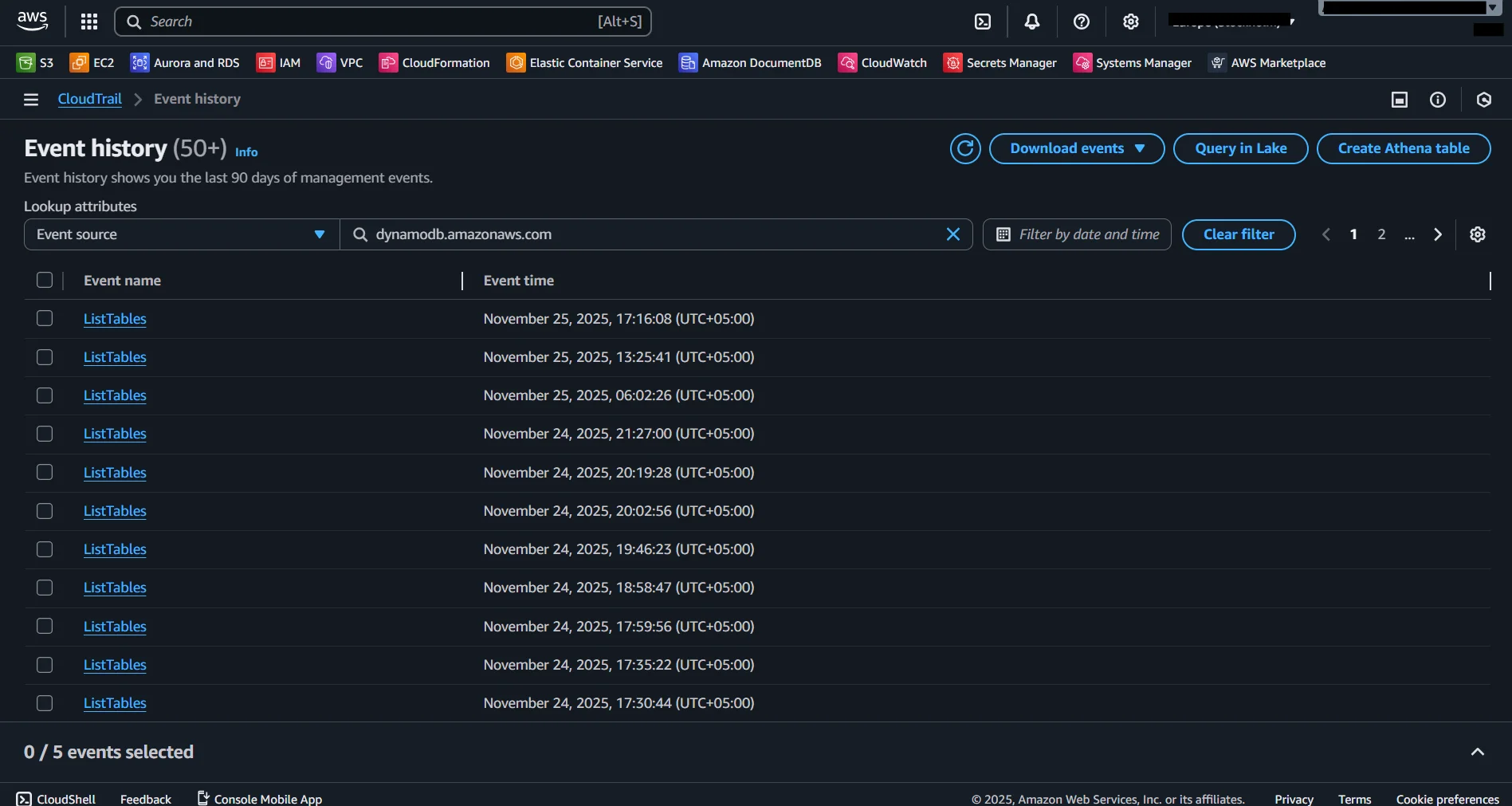
CloudTrail
CloudTrail records both administrative and data-access operations. Management events include table creation, deletion, auto-scaling adjustments, encryption configuration changes, and IAM updates affecting DynamoDB.
CloudTrail also tracks data-plane behavior such as GetItem, PutItem, DeleteItem, UpdateItem, and BatchWriteItem. These capabilities closely align with the centralized auditing logic described in Data Audit.
DynamoDB Streams
Streams provide a chronological record of data modifications — before-image and after-image snapshots, primary keys, and mutation types (INSERT, MODIFY, REMOVE). This level of detail complements CloudTrail and supports change tracking and forensic analysis.
Streams also enable:
- Real-time capture of item changes
- Replay of historical modifications
- Lambda-based event triggers
- Reconstruction of full item evolution
Conceptually, this corresponds with Data Activity History, which describes similar cross-platform behavior monitoring.
CloudWatch
CloudWatch enriches audit visibility with operational metrics. While not a direct audit feed, CloudWatch exposes spikes in read/write activity, throttling anomalies, latency issues, and unexpected error patterns.
Additionally, CloudWatch enables:
- Baseline-driven anomaly detection
- Infrastructure-related diagnostics
- Alerts and automation workflows
- Correlation of performance deviations with audit events
These insights complement User Behavior Analysis, which focuses on identifying anomalous usage patterns.
Enhanced DynamoDB Audit Logs with DataSunrise
DataSunrise consolidates CloudTrail, Streams, and mirrored-network observations into a single normalized audit model. This multi-source correlation is described in the DataSunrise Overview.
A unified audit plane eliminates AWS-native fragmentation and allows DynamoDB to be governed alongside SQL and NoSQL platforms with identical enforcement logic.
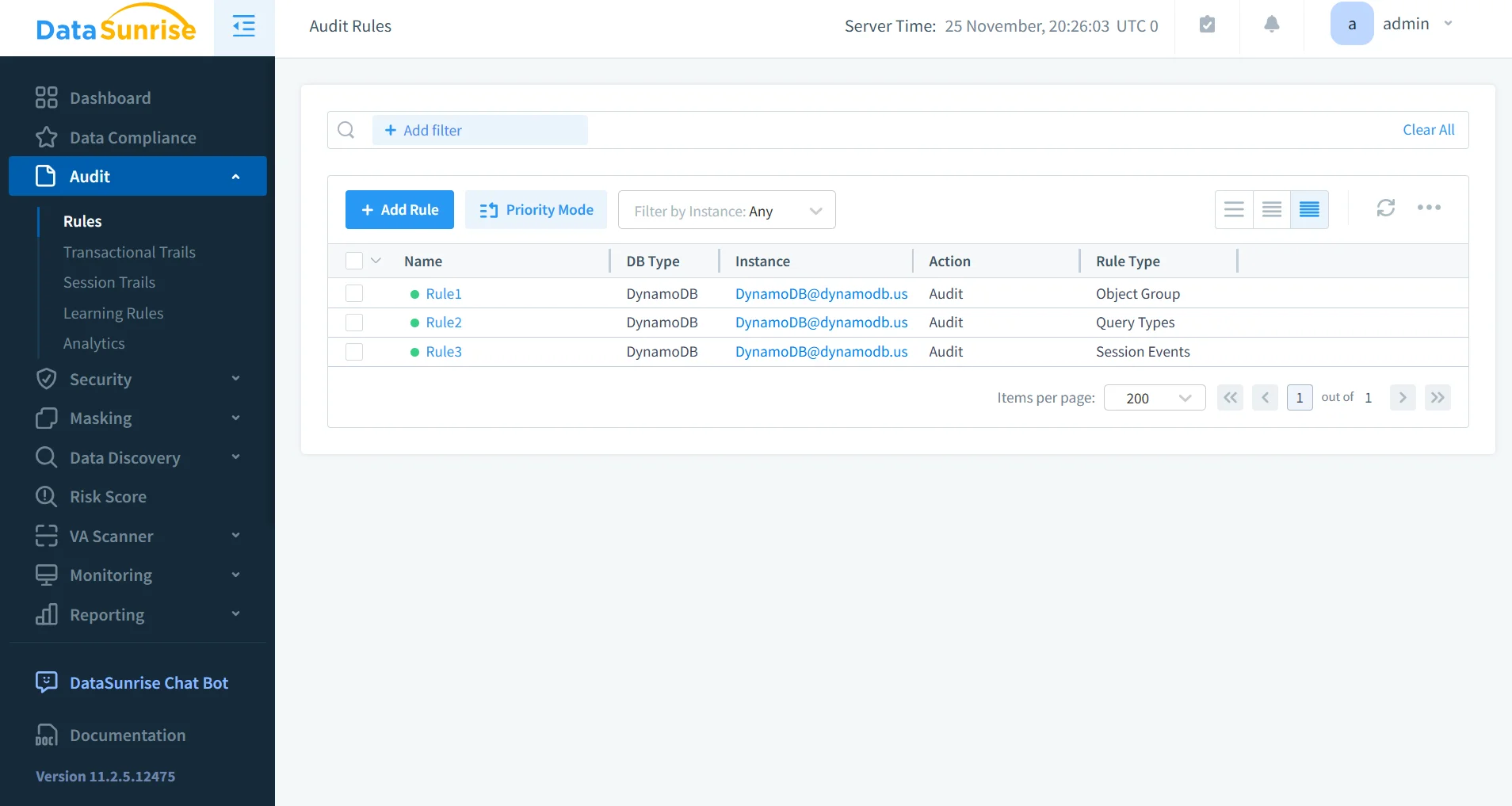
Audit Rules for DynamoDB
When DynamoDB logs arrive in DataSunrise, they are processed using the system’s rule engine. Organizations can define rules that trigger on sensitive data access, unusually large updates, session anomalies, unexpected regions, or patterns that resemble exfiltration attempts.
Best practices for rule design are documented in the Audit Guide.
Rules behave the same regardless of database engine, enabling unified governance across multi-platform deployments.
Real-Time Alerts and Masking
DataSunrise supports alert delivery through Slack, Microsoft Teams, email, SIEM platforms, and custom webhook channels. These alerts enable rapid triage and faster incident containment.
Dynamic masking ensures sensitive attributes are protected even inside audit logs. Full values remain visible only to privileged investigators. Masking models are detailed in Dynamic Data Masking.
For environments requiring long-term sanitized records, masking can be paired with Static Data Masking as part of a full lifecycle strategy.
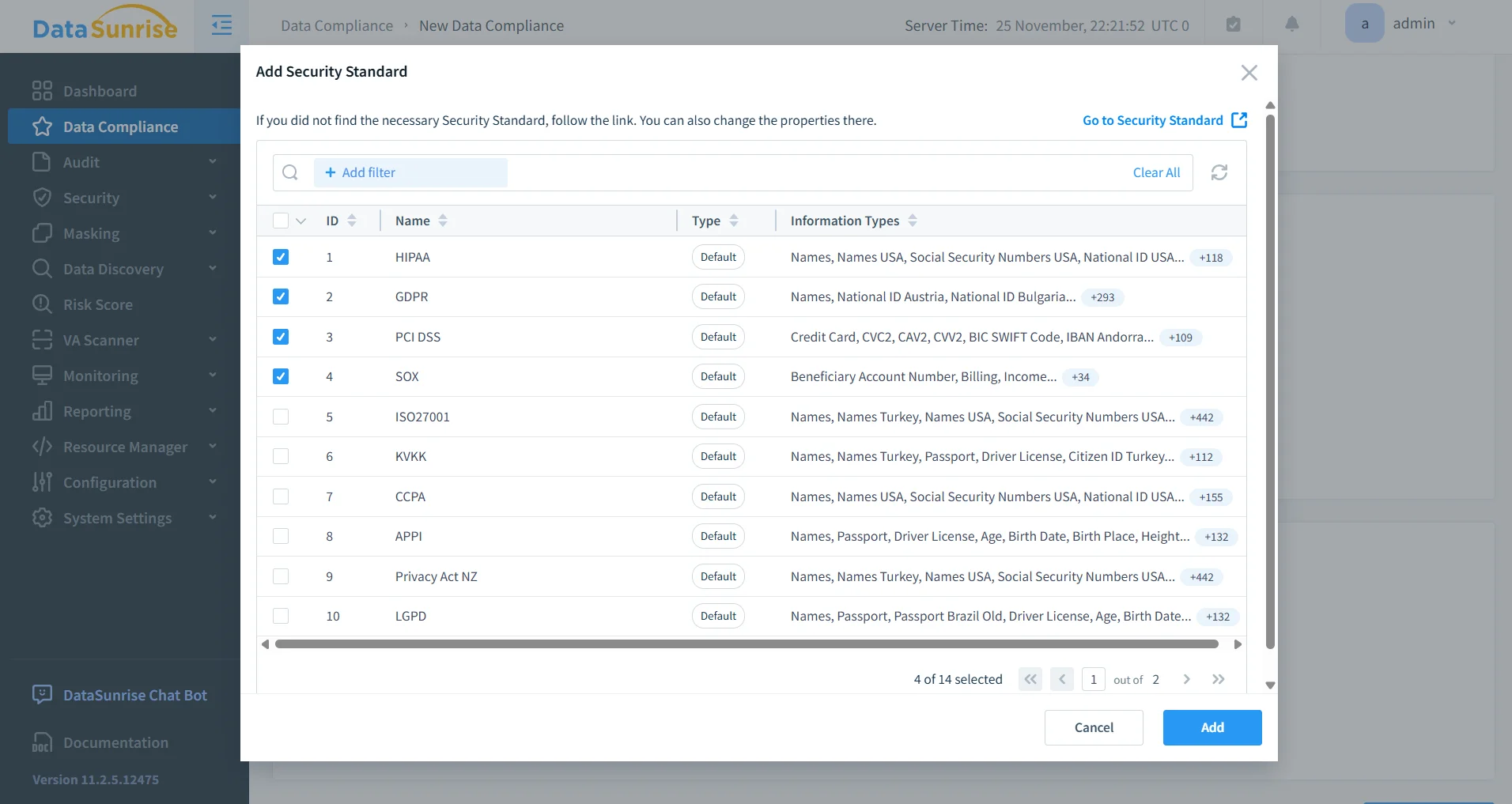
Compliance Alignment
AWS exposes raw audit events, but DataSunrise contextualizes them by mapping DynamoDB activity to regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
Compliance posture is automatically validated using the Compliance Manager.
This system also integrates with Data Compliance workflows for unified governance across all datasets.
Comparison Table
| Capability | Native DynamoDB Audit Logs | DynamoDB Audit Logs with DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility Across Platforms | Logs isolated within AWS services; no cross-platform correlation | Unified audit view across SQL, NoSQL, and cloud platforms |
| Investigation Speed | Manual parsing of CloudTrail, Streams, and CloudWatch | Rapid correlation of identities, operations, and data changes |
| Compliance Readiness | Raw log data with no regulatory mapping | Automated compliance reports aligned with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX |
| Real-Time Threat Detection | No built-in behavioral analysis | Behavior-based anomaly detection and real-time alerting |
| Sensitive Data Protection | Sensitive values may appear unmasked | Dynamic masking with role-based visibility control |
| Policy Enforcement | No ability to block or modify activity | Ability to block, alert, or mask based on rules |
| Operational Overhead | Requires manual Athena queries and scripting | Automated checks, centralized UI, and consistent governance |
| Scalability of Governance | Each table/account managed separately | Enterprise-wide rule management and drift detection |
Conclusion
DynamoDB provides foundational audit signals through CloudTrail, Streams, and CloudWatch, but these services alone cannot satisfy enterprise governance requirements. Organizations need normalization, masking, behavioral analytics, cross-system correlation, rule enforcement, and automated compliance evidence.
DataSunrise provides this entire lifecycle through its unified security platform, transforming DynamoDB into a fully governed, compliance-ready data system.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now