
Data Audit Trails

Introduction
A recent study by Tessian found that more than one-third of employees have unintentionally mishandled sensitive information during everyday work activities. Combined with research showing that over 88% of data breaches stem from human error, these findings underscore the critical importance of strong auditing and monitoring systems. Frequent mistakes—such as misdirected emails, cloud misconfigurations, or unintentional sharing of confidential documents—remain among the primary drivers of security incidents, particularly in hybrid and remote work environments.
In this context, maintaining a comprehensive and tamper-resistant audit trail has become indispensable for modern cybersecurity strategies. It ensures visibility across sensitive operations, supports accountability, accelerates incident response, and helps organizations meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Platforms like DataSunrise strengthen these capabilities by turning raw database activity data into meaningful insights—enabling early detection of anomalies, preventing data misuse, and improving overall security posture.
Clear data auditing practices and well-structured database security policies transform routine activity logs into high-value evidence that supports compliance management and effective incident investigation.
Why Audit Trails Matter Now More Than Ever
Audit trails have evolved far beyond being simple compliance checkboxes—they are now strategic enablers of data security, governance, and organizational transparency. In an era where insider risks, unauthorized data sharing, and shadow access continue to rise across complex hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures, maintaining a clear record of every user interaction and system event has become indispensable. Solutions like DataSunrise Activity Monitoring ensure that organizations can capture detailed activity even across distributed environments. Without a comprehensive audit trail, even the most advanced security tools struggle to provide accountability, context, or proof of compliance when it matters most.
A centralized, reliable, and tamper-proof audit trail enables security and compliance teams to transform raw activity data into actionable intelligence. By continuously monitoring user behavior, access patterns, and system changes, organizations gain real-time insight into what is happening across their databases—reducing uncertainty and improving overall control. Whether it’s preventing unauthorized access, supporting forensic investigations, or satisfying regulatory scrutiny, audit trails provide the visibility needed to make informed, defensible decisions.
With a robust audit framework in place, teams can:
- Hold users accountable for every action: Create a verifiable record of who did what, when, and from where—eliminating ambiguity and ensuring data stewardship.
- Accelerate incident response: Quickly reconstruct events to identify root causes, assess impact, and contain potential breaches before they escalate.
- Mitigate privilege creep and shadow access: Detect dormant or excessive permissions, ensuring that users have only the access they truly need. Controls such as DataSunrise Access Control help reinforce least-privilege enforcement.
- Prove compliance with confidence: Produce comprehensive, audit-ready reports that satisfy regulators and internal auditors without last-minute surprises.
As data landscapes expand and regulations tighten, the importance of audit trails will only continue to grow. They not only safeguard sensitive information but also build organizational trust, providing the foundation for responsible data governance and proactive cybersecurity defense.
What Is a Data Audit Trail?
At its core, a data audit trail is a structured, chronological record of activity involving sensitive data. It shows who accessed data, what changes occurred, and when deletions took place. In effect, it provides a complete view of data movement and modification, crucial for tracing unauthorized actions and validating internal processes.
| Field | Example | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| user_id | [email protected] | Ties every action to an identity |
| src_ip | 203.0.113.42 | Geolocation & anomaly checks |
| action | UPDATE | Fast filtering in SIEM rules |
| object | customers.ssn | Pinpoints sensitive assets |
| affected_rows | 1 024 | Bulk-export detection |
| status | success | Spot failed or denied attempts |
Audit Trail Glossary (Quick Reference)
- Transactional Trails
- DataSunrise’s indexed log of queries, users, sessions, and results—exportable as CSV or PDF, with optional SIEM integration.
- Data Classification
- Label PII, PHI, and PCI data to prioritize discovery, auditing, and masking efforts.
- RLS (Row-Level Security)
- Limits row access based on user roles—essential for enforcing least-privilege auditing at scale.
- SIEM
- Security Information and Event Management system that ingests audit logs for correlation, alerting, and threat detection.
- Week 1 – Discover — scan & classify sensitive tables
- Week 2 – Pilot — enable proxy logging on one database
- Week 3 – Alert — tune 3–5 anomaly rules, route to SIEM
- Week 4 – Automate — roll out masking & daily evidence packs
Ways to Implement Data Audit Trails
Using Built-In Database Tools
Most databases offer native audit logging features, which can track user sessions and record DML operations. While useful for basic scenarios, these tools often lack centralized oversight, multi-platform support, and real-time alerting.
-- PostgreSQL: Row-level data audit trail
CREATE TABLE data_audit_log (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
table_name TEXT,
action TEXT,
user_name TEXT,
old_data JSONB,
new_data JSONB,
executed_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT current_timestamp
);
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION audit_row_changes()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN
INSERT INTO data_audit_log(table_name, action, user_name, old_data, new_data)
VALUES (
TG_TABLE_NAME,
TG_OP,
session_user,
row_to_json(OLD),
row_to_json(NEW)
);
RETURN NEW;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_audit_changes
AFTER INSERT OR UPDATE OR DELETE ON sensitive_data
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION audit_row_changes();
# docker-compose.yml — portable audit lab
version: "3.8"
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:16
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: secret
volumes:
- ./init/:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/
datasunrise:
image: datasunrise/datasunrise:latest
ports:
- "11000:11000" # Web UI
- "5432:5432" # Proxy to Postgres
depends_on:
- postgres
Spin up Postgres + DataSunrise in one command for a local test drive.
Third-Party Platforms for Audit Management
Organizations often adopt external platforms for improved audit control. A solution like DataSunrise provides advanced filtering, customizable rules, real-time notifications, and centralized logging — everything essential for maintaining an enterprise-grade data audit trail.
Viewing Data Audit Trails in DataSunrise
- Log in to the web interface
- Navigate to “Instances” → “Add New Instance”
- Input database type and connection settings
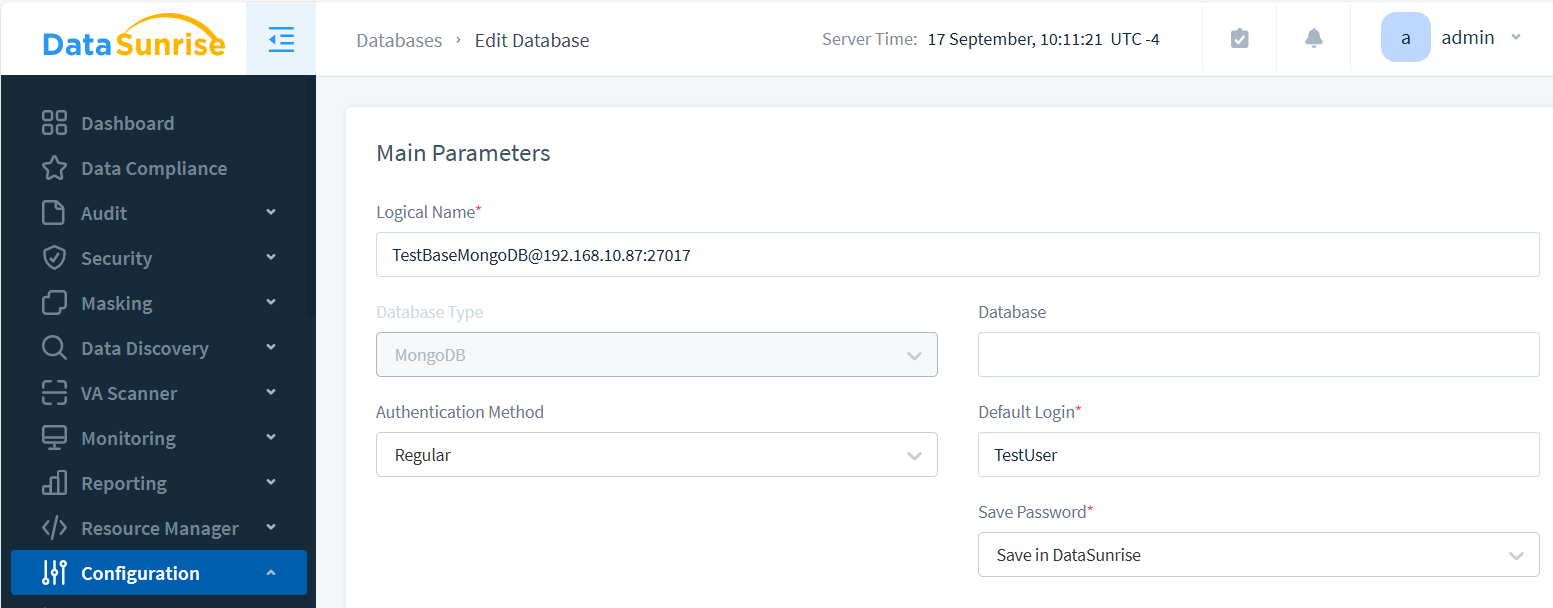
- Create and activate an audit rule
- Run sample queries to generate audit entries
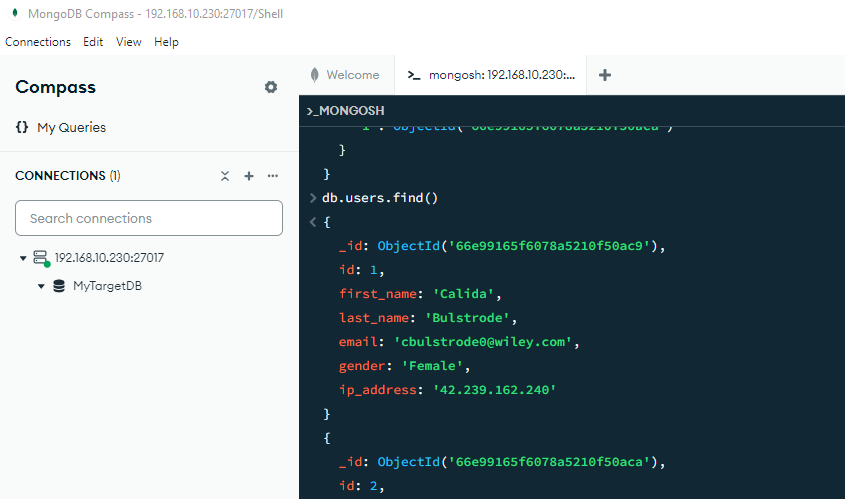
To review logs, navigate to “Audit → Transactional Trails.”
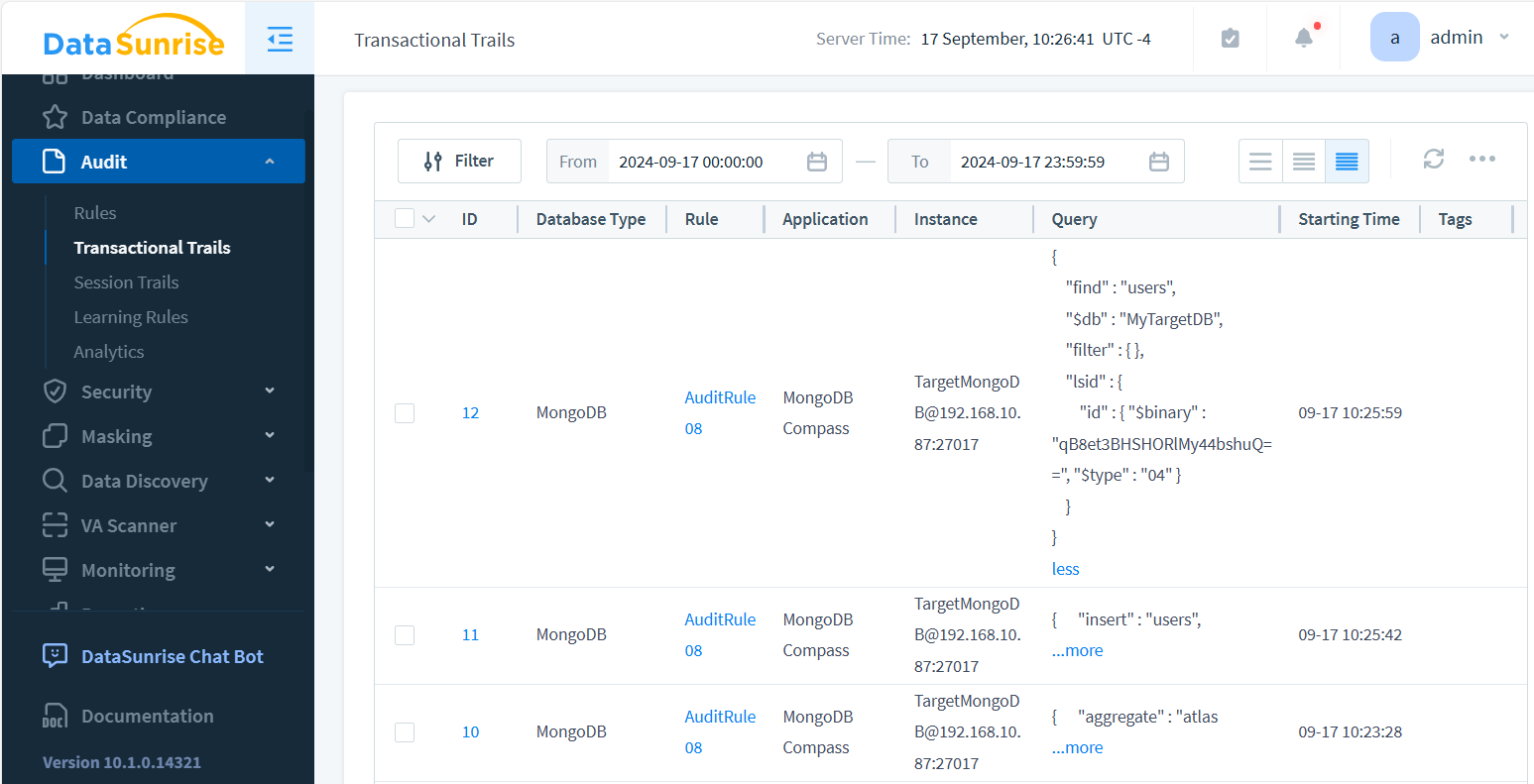
Audit Trail Example in MongoDB Enterprise
Common Audit-Trail Issues & Fixes
No logs appearing?
Confirm the proxy port is used by all apps and “Log Queries” is enabled in your rule.
High storage growth?
Enable result-set sampling or move cold logs to S3 with lifecycle policies.
Latency spikes after enabling triggers?
Batch-insert audit rows and set commit_interval = 5s to cut write I/O.
Requirements
- MongoDB Enterprise and Compass
- Admin rights on the MongoDB server
C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\7.0\bin\mongod.exe --version
Enable Auditing
mongod.exe --dbpath "C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\7.0\data\db" --auditDestination file --auditFormat JSON --auditPath "C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\7.0\data\db\auditLog.json"
Generate Events & Review
Perform actions in Compass or the CLI to trigger events, then check auditLog.json to see the results. Note: MongoDB Enterprise does not log read operations.
Why Regulators Care About Audit Trails
Audit trails are explicitly required by major compliance frameworks. GDPR mandates accountability and traceability of personal data, HIPAA enforces audit controls for PHI access, and PCI DSS Requirement 10 links every database action to an authenticated user. SOX demands proof of data integrity for financial systems. In each case, regulators expect clear, tamper-resistant evidence of user activity. Without a robust audit trail, organizations face compliance failures, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
Data Audit Trails in Compliance Frameworks
Major regulations define clear expectations for data audit trails. Mapping requirements ensures coverage and avoids gaps during audits:
| Framework | Audit Requirement | DataSunrise Capability |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Maintain logs of personal data use and provide traceability. | Granular rules with automated reporting for PII queries. |
| HIPAA | Log all PHI access and generate tamper-resistant evidence. | Centralized trails tagged with PHI and protected via integrity checks. |
| PCI DSS | Link each access to authenticated users; detect anomalies in cardholder data usage. | Real-time alerts, classification of PCI fields, and SIEM integration. |
| SOX | Trace privilege changes and financial record modifications with accuracy. | Detailed rule-based logging with auditor-ready exports (CSV, PDF). |
By aligning audit trails with these frameworks, DataSunrise Database Audit turns logs into compliance-ready evidence, reducing manual prep time and strengthening regulatory posture.
Advantages of Centralized Data Audit Trail Tools
- Unified audit control across multiple database platforms
- Advanced filtering for rapid event triage
- Real-time alerting via Slack or email integration
- Out-of-the-box reports for PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR
- Scalable storage and high-throughput event capture
Native Logging vs. DataSunrise: What’s the Difference?
| Capability | Native DB Logging | DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Platform Audit | No | Yes |
| Real-Time Alerts | No | Yes |
| Data Classification Integration | No | Yes (PII, PCI, custom types) |
| Exportable Reports (PDF, CSV) | Manual | Yes |
| Audit Policy Granularity | Limited | Column-, role-, time-, or query-based |
How to Build a Robust and Actionable Audit Trail
Logging Scope
Not all data needs to be monitored equally. Focus your audit trail on high-risk data domains—such as financial records, healthcare information, authentication tokens, or personal identifiers. Prioritize operations like SELECT (especially on sensitive columns), INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE on core tables, and privilege escalations. This focused approach reduces log noise, improves searchability, and minimizes storage overhead. In multi-tenant systems, scope logs per client or schema to maintain clarity across environments.
Integrity & Retention
An audit trail is only as good as its trustworthiness. Store logs in tamper-resistant formats—either using immutable storage or cryptographic hashes that verify integrity. Consider layering in secure backup mechanisms or offloading to external storage like Redshift, S3, or Azure Blob with versioning. Align retention schedules with the strictest regulation that applies to your business (e.g., 6 years for SOX, rolling 12 months for PCI DSS). Retention also depends on your internal forensics and legal review windows—balance regulatory compliance with operational capacity.
Alerting & Detection
Modern audit systems must move beyond passive recordkeeping. Implement alerting rules that flag anomalies like access outside business hours, bulk exports, or access from unfamiliar geolocations. Leverage session metadata and identity context to enrich alerts before forwarding to SIEM platforms. Consider integrating with tools like Slack or PagerDuty to push high-priority events directly to response teams. When set up right, your audit trail becomes an active threat detection mechanism, not just a post-mortem tool.
# Forward DataSunrise events to AWS CloudWatch Logs
aws logs put-log-events \
--log-group-name "datasunrise-audit" \
--log-stream-name "prod-db-01" \
--log-events "timestamp=$(date +%s%3N),message='${JSON_PAYLOAD}'"
Compliance Alignment
Each regulation has specific audit requirements. GDPR mandates transparency and traceability of personal data usage. HIPAA requires access audits for protected health information. PCI DSS mandates linking each event to an authenticated user. Design your audit schema to log user identity, source IP, action type, target object, and result status for each event. Build standardized report templates for audit teams and regulators, and automate generation to reduce manual workload before audits.
Want to catch threats in real-time?
Try our interactive demo and see how DataSunrise’s alerting, masking, and audit trail systems work together to provide layered protection and compliance visibility in one pane.
Quick Start: Minimal Data Audit Trail Pipeline (30 minutes)
This guided sequence standardizes collection and routing so you can validate an end-to-end audit trail quickly, then scale. It complements native logging and centralizes evidence for investigations and compliance.
Prerequisites
- Access to one database (e.g., PostgreSQL/SQL Server/MySQL) and a non-prod schema
- DataSunrise instance with console access (Database Audit, Activity Monitoring)
- One destination for events (SIEM, CloudWatch, or similar)
Steps
- Scope the target objects. Start with one high-risk table and two actions (e.g.,
SELECTandUPDATE) to keep signal-to-noise high. - Register the database in DataSunrise. Console → Instances → Add New Instance → provide connection details. Verify connectivity.
- Create an Audit rule. Audit → Rules → select objects and actions. Enable query logging; optionally capture parameters only for sensitive columns.
- Route events to your SIEM. Configure an outbound connector or HTTP endpoint. Example (Splunk HEC):
# Send a test event (replace URL/TOKEN)
curl -k https://splunk.example:8088/services/collector \
-H "Authorization: Splunk $HEC_TOKEN" \
-d '{"event":{"source":"datasunrise","action":"select","object":"public.customers","actor":"app_reader","status":"success"}}'- Generate activity. Run a simple query against the scoped table to produce at least three events (read, write, denied).
- Verify in DataSunrise. Audit → Transactional Trails → confirm timestamps, actor, object, action, status. Cross-check in SIEM.
- Lock in integrity & retention. Enable immutable/WORM on cold storage or add a hash-chain check (see the page’s “Tamper-Evident” section).
Optional: Enable pgaudit (PostgreSQL)
# postgresql.conf shared_preload_libraries = 'pgaudit' pgaudit.log = 'read,write,ddl' pgaudit.log_parameter = on -- In SQL (per DB) CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pgaudit;
Go/No-Go KPIs for this pilot
- Coverage: 100% of scoped objects/events appear in trails
- MTTD (pilot): < 5 minutes from event to alert
- Noise ratio: < 20% non-actionable events
- Integrity checks: zero failures over 24 hours
Native Audit Examples Beyond PostgreSQL
Every database family has its own audit logging quirks. Below are two common approaches security teams often rely on before moving to centralized solutions:
SQL Server: File-Based Auditing
-- Enable audit writing to file
CREATE SERVER AUDIT AuditFile
TO FILE (FILEPATH = 'C:\SQLAudits\', MAXSIZE = 500 MB, MAX_ROLLOVER_FILES = 10)
WITH (ON_FAILURE = CONTINUE);
ALTER SERVER AUDIT AuditFile WITH (STATE = ON);
-- Capture read/write activity in a database
CREATE DATABASE AUDIT SPECIFICATION AuditSpec
FOR SERVER AUDIT AuditFile
ADD (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON DATABASE::FinanceDB BY PUBLIC)
WITH (STATE = ON);
-- Quick read-back
SELECT event_time, server_principal_name, statement
FROM sys.fn_get_audit_file('C:\SQLAudits\*.sqlaudit', DEFAULT, DEFAULT)
ORDER BY event_time DESC;
MySQL Enterprise: JSON Audit Log
-- Enable the audit plugin
INSTALL PLUGIN audit_log SONAME 'audit_log.so';
-- Log everything in JSON format (scope down in prod)
SET PERSIST audit_log_format = JSON;
SET PERSIST audit_log_policy = ALL;
-- Verify plugin state
SHOW PLUGINS LIKE 'audit%';
-- Audit logs written to
/var/lib/mysql/audit.log
Native logs are useful, but every DBMS outputs different formats. Correlation across platforms quickly becomes a manual burden.
Real-World Outcomes of Data Audit Trails
| Outcome | Native Logs | With DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Audit Prep Time | Manual exports (days) | Automated, export-ready (hours) |
| Incident Detection | Reactive, post-breach | Real-time alerts with session context |
| Compliance Coverage | Partial, DB-specific | Cross-platform, 100% schema coverage |
Who Benefits?
- Finance: Trace unauthorized trades and insider access (SOX)
- Healthcare: Monitor PHI handling for HIPAA audits
- SaaS Providers: Prove tenant isolation and accountability
- Government: Strengthen data access transparency
Making Audit Trails Tamper-Evident
For compliance, it’s not enough to collect logs—you must also prove they haven’t been altered. One simple pattern is chaining cryptographic hashes across audit rows in PostgreSQL:
-- Requirements: pgcrypto extension
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pgcrypto;
-- Append-only table
CREATE TABLE audit_chain (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
actor TEXT,
action TEXT,
ts TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
prev_hash BYTEA,
row_hash BYTEA
);
-- Hash-chain insert
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION audit_chain_append()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
DECLARE
v_prev BYTEA;
BEGIN
SELECT row_hash INTO v_prev FROM audit_chain ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT 1;
NEW.prev_hash := v_prev;
NEW.row_hash := digest(coalesce(NEW.actor,'')||'|'||coalesce(NEW.action,'')||'|'||coalesce(NEW.ts::text,'')||encode(coalesce(NEW.prev_hash,'\x'),'hex'), 'sha256');
RETURN NEW;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
CREATE TRIGGER trg_chain
BEFORE INSERT ON audit_chain
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION audit_chain_append();
-- Integrity check
WITH ordered AS (
SELECT id, row_hash, prev_hash,
lag(row_hash) OVER (ORDER BY id) AS expected_prev
FROM audit_chain
)
SELECT * FROM ordered WHERE prev_hash IS DISTINCT FROM expected_prev;
The query at the end must return no rows. Any output signals tampering or chain breakage.
Modern Architecture for Scalable Data Audit Trails
Designing an effective data audit trail system goes beyond simply logging events—it requires a well-architected approach that balances performance, compliance, and incident response. Below are the core layers you should consider in any modern deployment:
- Logging Layer: Capture DML, DDL, and authentication events from databases, APIs, and data lakes. Use agents, triggers, or proxy-based platforms like DataSunrise to avoid missing critical activity.
- Storage Layer: Retain logs in immutable or versioned storage such as Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, or append-only PostgreSQL tables. Enable encryption and fine-grained access control.
- Parsing & Normalization: Convert heterogeneous logs into a common schema—user, action, target object, result, timestamp, and source. This simplifies querying, filtering, and compliance audits.
- Detection & Alerting: Correlate log data with behavioral models to flag anomalies like bulk queries, odd login times, or unauthorized schema changes. Integrate with SIEMs or SOAR platforms for escalation.
- Reporting & Retention: Generate audit-ready outputs for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. Store logs according to your longest applicable retention window and ensure tamper-evidence with checksums or blockchain append-only techniques.
Enterprises that architect their data audit trail with scalability and automation in mind are better prepared for forensic investigations, regulator scrutiny, and insider threat response. A reactive log system is no longer enough—your audit trail must be proactive, adaptive, and provable.
The Future of Data Audit Trails
Audit trails are evolving from static records into proactive defense systems. Key trends include:
- AI-Driven Anomaly Detection: Machine learning models surface unusual query patterns that traditional rules may miss.
- Zero-Trust Enforcement: Continuous verification of every user action, regardless of role or location.
- Immutable Storage: Blockchain and hash-chaining ensure tamper-proof logs for regulatory audits.
- Automated Compliance Pipelines: Pre-built policies that map directly to frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Organizations adopting these capabilities move from reactive evidence gathering to predictive security and continuous compliance.
Conclusion
Robust audit trails are essential for ensuring data transparency, accountability, and long-term organizational stability. By capturing not only the actions taken within a system but also the relevant context — including user identity, timing, and impacted assets — they enable security and compliance teams to accurately retrace events and uncover the root causes of incidents. This depth of visibility strengthens early anomaly detection, improves response accuracy, and supports full adherence to internal governance standards as well as external regulatory requirements.
Although built-in logging tools provide a foundational level of insight, they often fall short in terms of scalability, analytic sophistication, and automation for enterprise-class needs. Advanced solutions like DataSunrise address these gaps with intelligent monitoring, unified visibility across databases, and real-time alerting across diverse infrastructures. They help organizations centralize governance workflows, simplify audit preparation, and bolster data security — all without impacting performance. To see these capabilities in action, explore our interactive demo or visit the product overview to understand how DataSunrise strengthens compliance and security strategies in today’s evolving data environment.
