Data Masking in Amazon OpenSearch
Data masking in Amazon OpenSearch is a practical way to reduce sensitive data exposure without breaking the search, analytics, and observability workflows that teams rely on. OpenSearch clusters often ingest authentication events, customer activity logs, application payload fragments, and operational telemetry. Those datasets frequently include personally identifiable information (PII), account identifiers, IP addresses, and other regulated elements—sometimes embedded inside unstructured log messages or nested JSON.
AWS provides the managed platform for Amazon OpenSearch Service, but compliance accountability remains with the organization operating the data. In compliance terms, it doesn’t matter that the data is “only in logs.” If it’s indexed and searchable, it’s subject to governance and audit expectations.
This article explains what data masking is, why OpenSearch needs masking beyond native access controls, and how DataSunrise enables dynamic masking, discovery-driven policy scoping, auditing, and reporting for OpenSearch environments.
What Data Masking Means for OpenSearch
At a high level, data masking replaces sensitive values with safer representations while preserving usability. Unlike encryption at rest (which protects storage), masking protects what users actually see in query results. A helpful overview is available here: What is Data Masking.
In OpenSearch, masking is especially valuable because:
- Indices commonly store semi-structured documents with sensitive fields scattered across payloads.
- Dashboards and alerts often require broad read access to keep operations running.
- Once a query is allowed, returning raw values can violate least-privilege expectations.
Why Native OpenSearch Controls Are Not Enough
Amazon OpenSearch supports strong authentication and authorization patterns, and many organizations use fine-grained access control to restrict index or field access. However, access control alone does not solve “need-to-know visibility.” In many cases, users must query an index to perform their job, but they do not need raw personal identifiers in the output.
This is the gap masking fills: it preserves operational visibility (search relevance, aggregations, dashboards) while reducing exposure of sensitive values.
Dynamic vs. Static Masking for Amazon OpenSearch
A strong masking strategy usually combines two approaches:
- Dynamic masking (mask at query time): values are transformed when returned to the requester, based on identity, role, or context. See Dynamic Data Masking.
- Static masking (mask at rest for copies): values are transformed in exported datasets or non-production copies used for testing, analytics, or development. See Static Data Masking.
In OpenSearch environments, dynamic masking is often the fastest win because it protects production access paths immediately—without rebuilding pipelines or maintaining parallel indices.
How DataSunrise Enables Masking for Amazon OpenSearch
DataSunrise provides a centralized security and compliance layer that can apply masking rules, auditing, and reporting consistently across OpenSearch environments. The workflow typically looks like this:
- Discover sensitive fields and patterns across indices.
- Scope policies to specific indices, documents, and fields that actually require protection.
- Apply dynamic masking rules for query results based on users/roles and access intent.
- Audit all relevant activity and generate compliance-ready evidence.
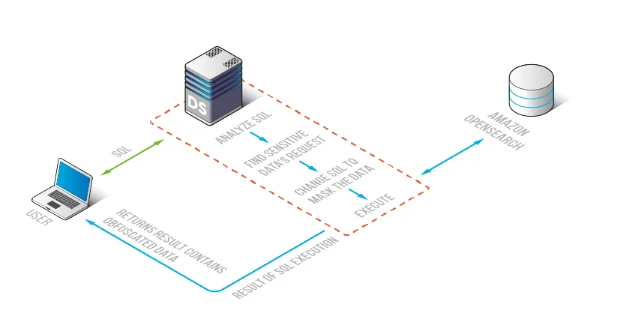
DataSunrise applies masking rules so OpenSearch queries can remain functional while sensitive values are obfuscated in results.
Step 1: Discover Sensitive Data in OpenSearch
Masking rules are only as good as your data inventory. OpenSearch data changes constantly—new fields appear, pipelines evolve, and “temporary” debug logs become permanent. Automated discovery is the most reliable way to keep pace.
DataSunrise Data Discovery helps identify sensitive patterns, including PII, across OpenSearch indices and documents. Discovery results can directly inform which objects should be governed and which fields should be masked.
Discovery-driven masking also supports regulated programs aligned with data compliance regulations and common frameworks such as GDPR compliance, HIPAA compliance, and PCI DSS compliance.
Step 2: Scope Masking to the Right Indices and Fields
A frequent operational mistake is applying security controls too broadly and breaking dashboards. Masking should be scoped precisely: only where sensitive values exist, and only for roles that should not see raw values.
This approach is easiest to operationalize when paired with clear role-based access control (RBAC) and the principle of least privilege. The compliance program itself can be managed centrally through Compliance Manager.
Step 3: Configure Dynamic Masking Rules
Dynamic masking rules define how sensitive values are transformed at query time. Depending on your governance model, masking can be applied to specific roles (for example, support analysts), environments (production vs. staging), or query sources. Common masking outcomes include full redaction, partial masking, or normalization where only the minimum necessary information remains visible.
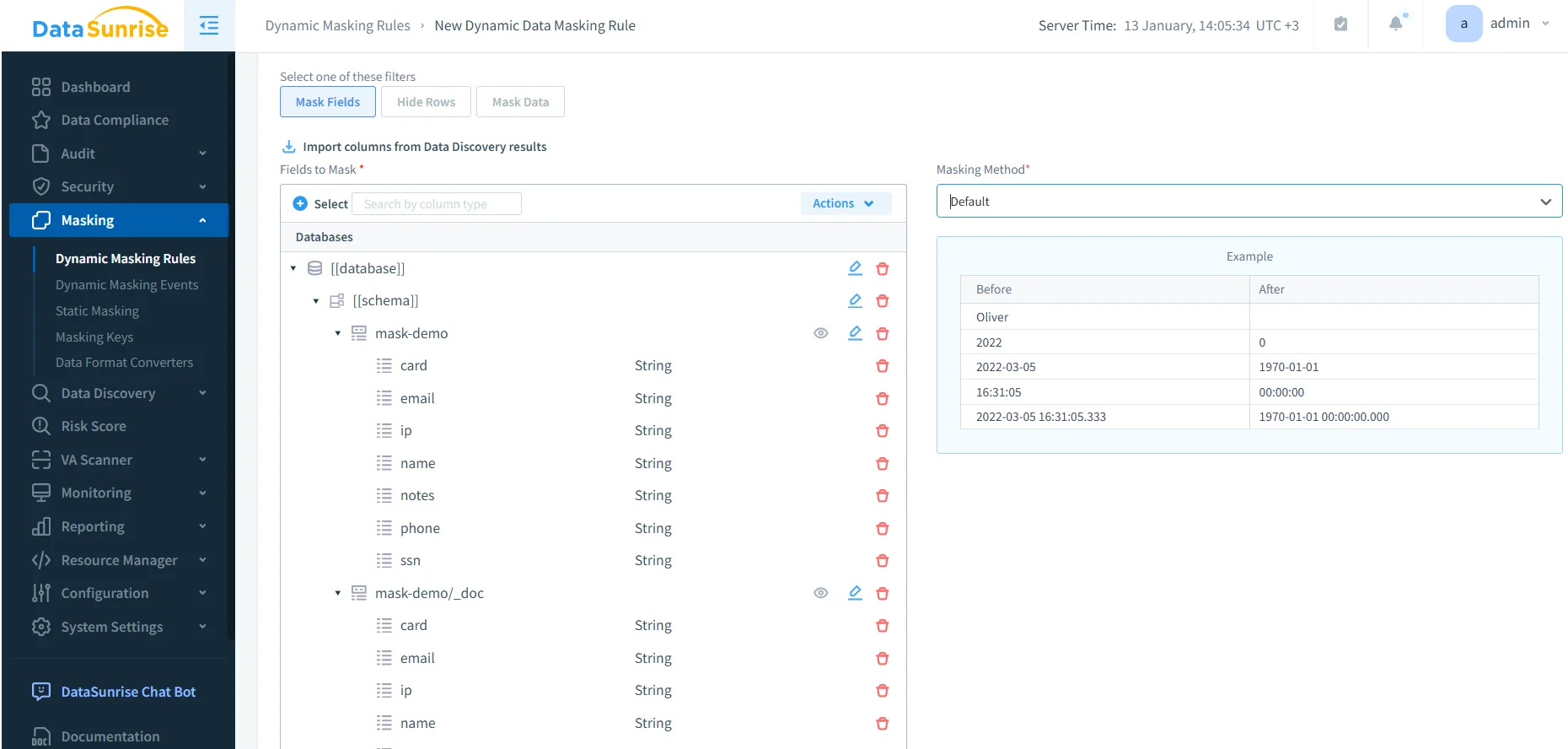
Creating a dynamic masking rule: select fields to mask and choose the masking method for governed OpenSearch data.
In practice, successful masking programs include:
- Field-level targeting: mask only the fields that contain sensitive values.
- Role-aware visibility: allow privileged roles to see full values when justified, and mask for everyone else.
- Deterministic enforcement: resolve policy overlap with predictable evaluation order.
When multiple controls apply, consistent enforcement depends on rule precedence. DataSunrise supports deterministic behavior through rules priority.
Step 4: Audit Masked Access and Preserve Evidence
Masking is a security control, but compliance requires evidence. You need to prove that sensitive values were protected and that access was logged consistently across environments.
DataSunrise provides centralized Data Audit, detailed audit logs, and immutable audit trails. For ongoing oversight, database activity monitoring helps identify unusual patterns such as bulk extraction attempts, repeated lookups of sensitive fields, or anomalous access sources.
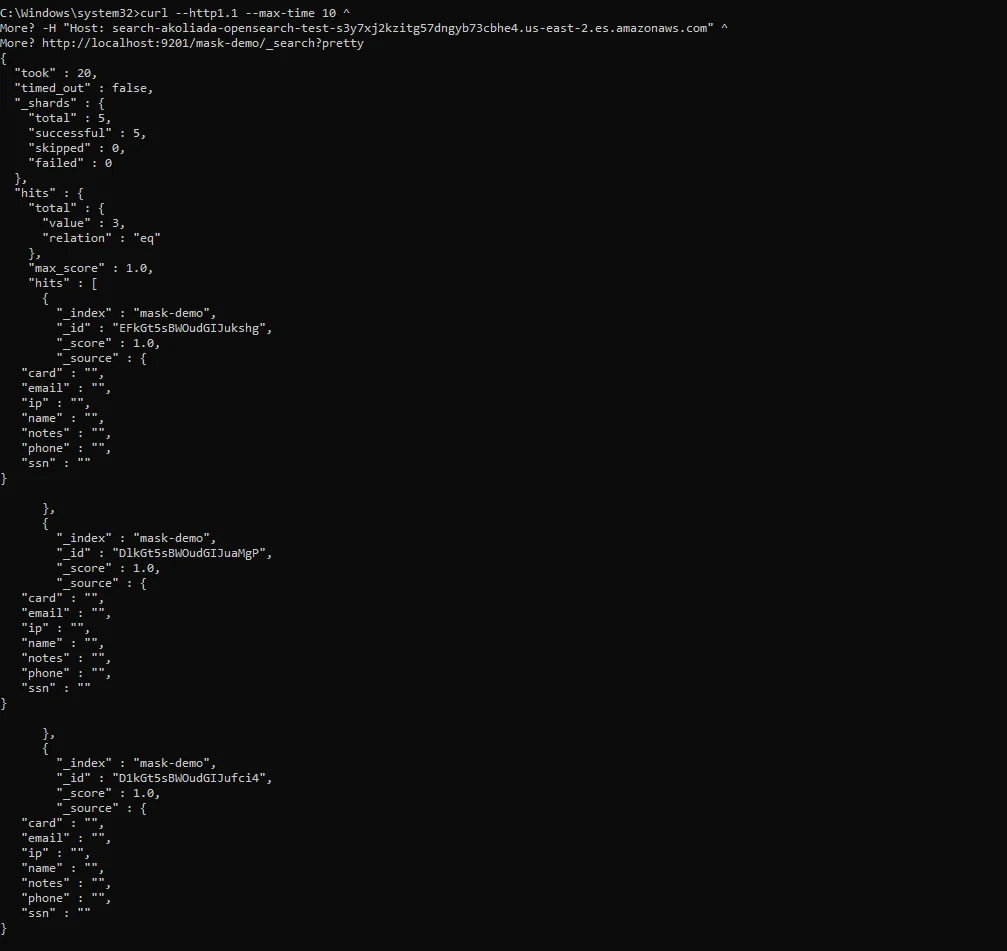
Auditing masked access: query outputs show obfuscated values while activity remains traceable for investigations and audits.
AWS also provides service-level logging features as a baseline reference. See Amazon OpenSearch audit logs. However, compliance programs often require consistent evidence and unified control points across multiple environments and access paths.
Hardening Masking with Preventive Security Controls
Masking reduces exposure, but it should not be the only line of defense. Strong programs pair masking with preventive controls that reduce risk from abuse, misconfiguration, and drift.
- Database firewall rules to block abusive query patterns.
- Vulnerability assessment to detect configuration weaknesses and drift.
- Continuous data protection to keep controls active as OpenSearch environments evolve.
Reporting: Turning Masking Controls into Compliance Proof
Auditors rarely accept “we enabled masking” as proof. They want evidence that controls exist, are applied consistently, and remain active over time. DataSunrise supports compliance evidence packaging through report generation, consolidating discovery results, masking policies, and audit activity into review-ready outputs.
Masking works best when it is discovery-driven and role-aware. Start with automated discovery, scope rules to sensitive indices, and apply dynamic masking to roles that do not require raw identifiers.
Do not index secrets (API keys, session tokens, passwords) into OpenSearch and assume masking will “clean it up later.” Searchable secrets are a fast exfiltration path. Prevent them at ingestion and enforce strict scope, auditing, and access controls immediately.
Conclusion: Make OpenSearch Masking Operational, Not Occasional
Data masking in Amazon OpenSearch is a practical, high-impact control for reducing sensitive data exposure while keeping search and analytics functional. The most effective approach combines discovery, scoped policy enforcement, dynamic masking at query time, and audit-ready evidence collection—so compliance remains continuous rather than reactive.
To explore implementation options, review the DataSunrise overview, compare deployment modes, and start with a demo or a download for evaluation.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now