How to Audit Google Cloud SQL
Introduction
Google Cloud SQL is a managed service for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. Auditing in Cloud SQL helps you prove accountability, spot anomalies, and satisfy requirements from regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. An effective audit trail records logins, query activity, schema changes, and permission updates. It supports investigations, reduces blind spots across instances, and gives teams evidence they can share with auditors.
This guide shows how to configure native auditing for SQL Server on Cloud SQL, review and centralize logs, and extend the setup with DataSunrise for real-time monitoring, masking, discovery, and audit-ready reporting. You’ll see how to enable SQL Server Audit on Cloud SQL, export .sqlaudit files to Cloud Storage, search events in Cloud Logging, and analyze trends in BigQuery. Then we layer on DataSunrise to add instant alerts, role-aware masking for sensitive fields, automated compliance reports, and a single view across multiple Cloud SQL instances.
What an Audit Trail Captures
An audit trail in Cloud SQL should cover every action that can affect data integrity or access. It’s not just what happened, but also who, when, where, and to which object.
- Access events — Successful and failed logins, session starts/ends, privilege escalations. Useful for spotting brute-force attempts and off-hours access by privileged accounts.
- Queries —
SELECTstatements on sensitive tables, ad-hoc exports, long-running reads. Helps you see who viewed PII and how often data leaves its source. - Modifications —
INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE, bulk loads. Lets you tie specific data changes to a user, session, and time window. - Schema operations —
CREATE,ALTER,DROPfor tables, views, procedures, or indexes. Critical for detecting drift and unauthorized structural changes. - Permission changes —
GRANT,REVOKE, role membership edits. Shows when access widened and who approved it.
Two practical notes: keep retention long enough to cover your investigation window and audits (often 90–365 days), and avoid exposing sensitive values in downstream tools—use masking where possible so audit visibility doesn’t become a new leak path.
Quick Start: Native SQL Server Audit on Cloud SQL
Create a server audit
CREATE SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
TO FILE (FILEPATH = '/var/opt/mssql/audit', MAXSIZE = 100 MB);
ALTER SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit WITH (STATE = ON);
Monitor reads on a sensitive table (database scope)
CREATE DATABASE AUDIT SPECIFICATION AuditTransactions
FOR SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
ADD (SELECT ON dbo.transactions BY public)
WITH (STATE = ON);
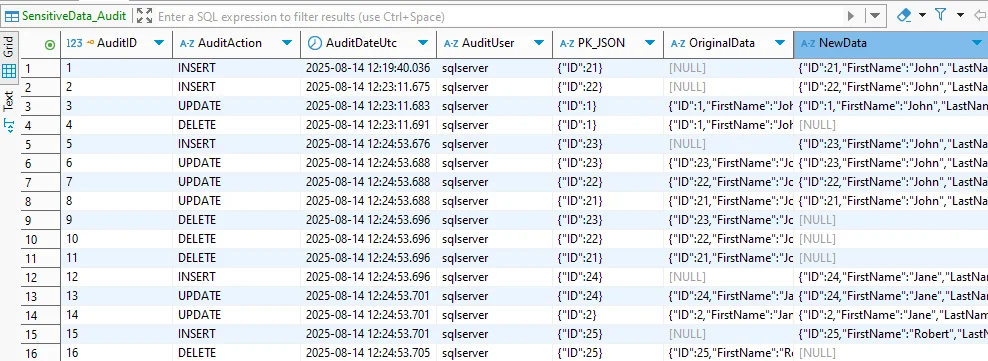
Review audit data
Use the Cloud SQL helper (works great with your screenshots):
SELECT TOP (200)
event_time,
action_id,
succeeded,
server_principal_name,
database_name,
statement,
object_name,
session_id,
additional_information
FROM msdb.dbo.gcloudsql_fn_get_audit_file('/var/opt/mssql/audit/*', NULL, NULL)
ORDER BY event_time DESC;
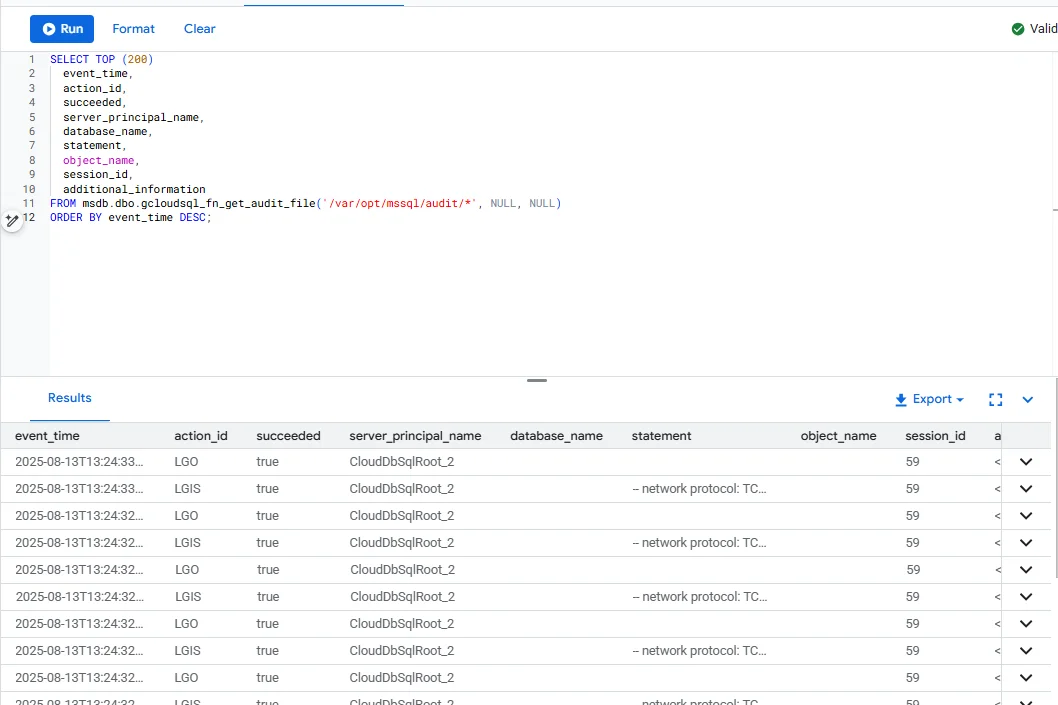
Or the standard SQL Server function:
SELECT *
FROM sys.fn_get_audit_file('/var/opt/mssql/audit/*.sqlaudit', NULL, NULL);
Centralize and Analyze Audit Logs
- Export
.sqlauditfiles from/var/opt/mssql/auditto Cloud Storage for low-cost retention. - Ingest audit events into Cloud Logging to search and correlate with other GCP logs.
- Load into BigQuery for trend analysis, dashboards, and long-term analytics.
Tip: keep instance and exporter jobs in the same VPC, and protect access with IAM and per-bucket lifecycle rules.
Limitations of Native Tools
| Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|
| No real-time alerting | Teams only react after reviewing logs |
| Sensitive data appears in plain text | Risk if logs are exposed |
| Siloed by instance | Hard to correlate across many Cloud SQL servers |
| Static audit scope | New sensitive tables need manual reconfiguration |
| Minimal reporting automation | Extra work to produce compliance-ready reports |
Extend Auditing with DataSunrise
DataSunrise adds an actionable layer on top of your Cloud SQL audit pipeline. It centralizes oversight, enforces controls in real time, and produces evidence you can hand to auditors—without changing applications.
Rule scope & precision
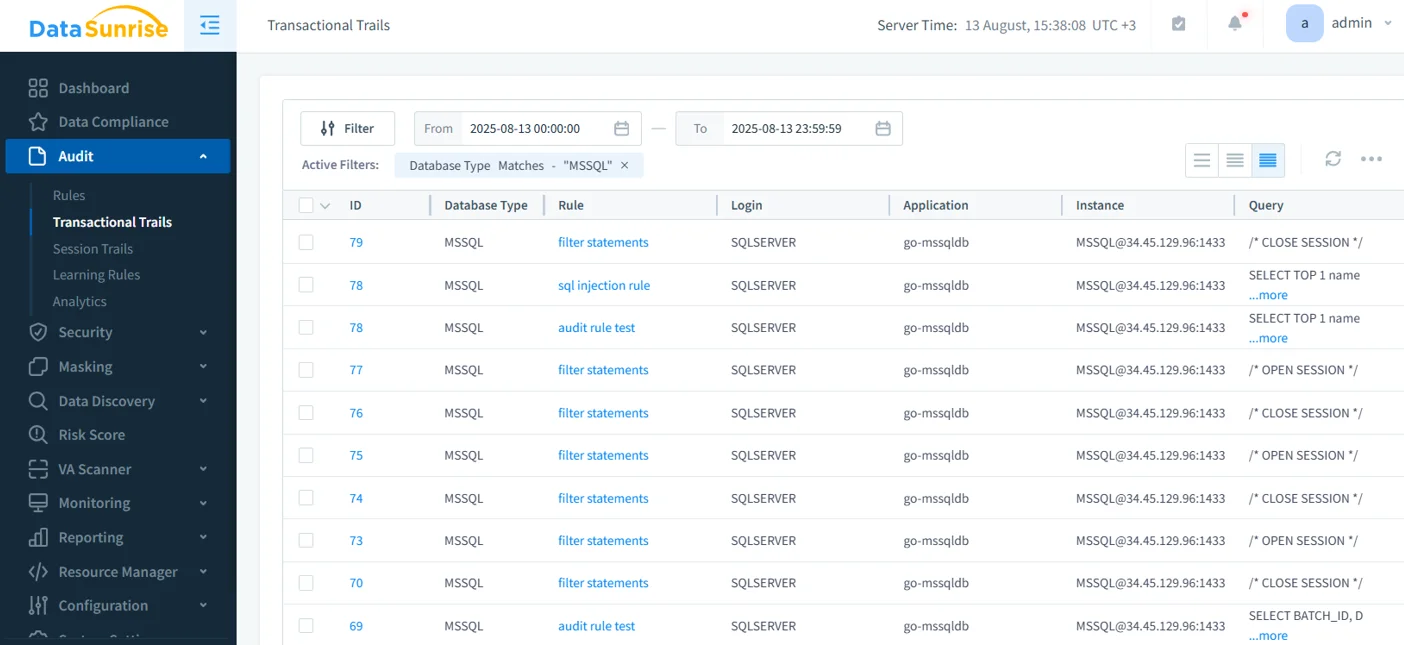
Use Granular audit rules to define exactly what to capture at the database, schema, table, column, and action level. Narrow by user, role, IP range, client app, or statement pattern to cut noise. Typical uses include focusing on SELECT against PII tables, blocking mass exports, or tracing privileged activity.
Live monitoring & alerts
Real-time monitoring watches queries as they happen and triggers alerts to SIEM, email, or Slack. Set thresholds and anomaly rules for brute-force logins, off-hours access, unusual row counts, or sudden spikes in reads. This turns audits from a retrospective log into a live control.
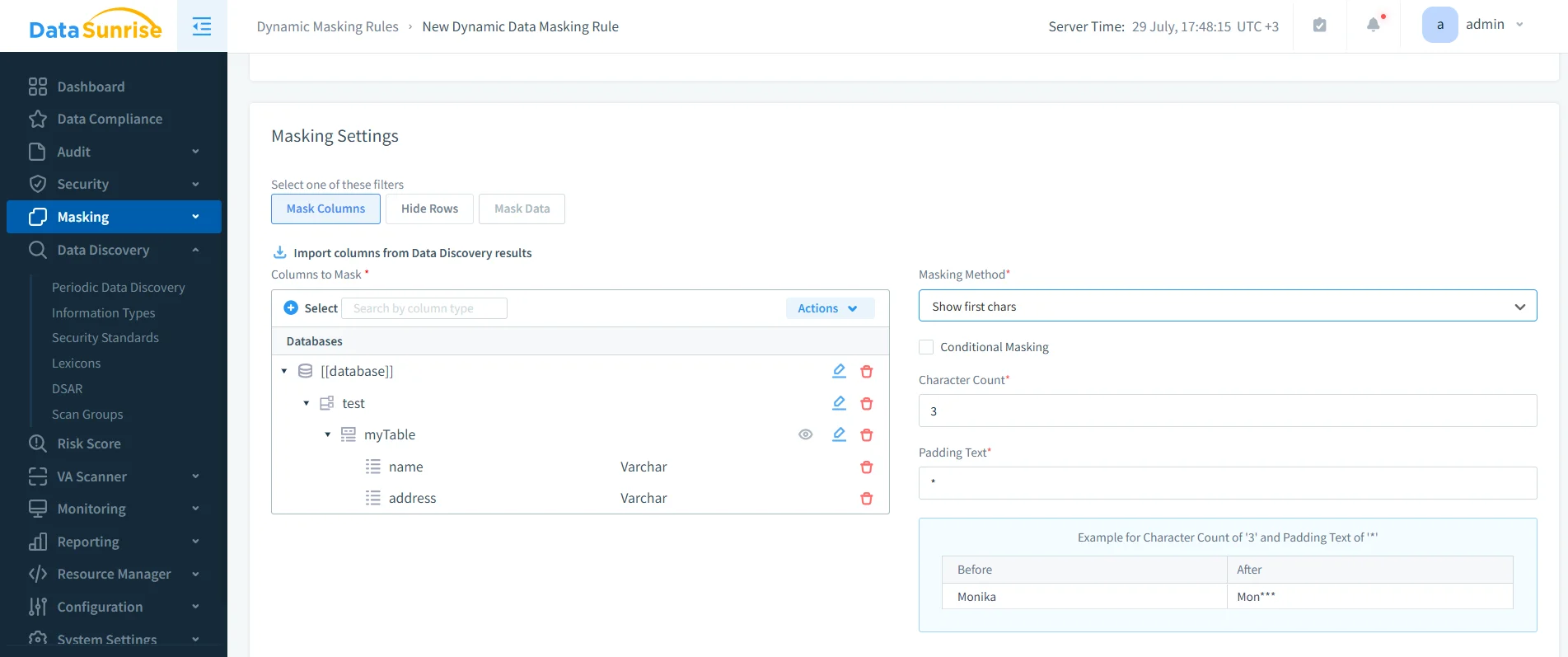
On-the-fly masking
Dynamic data masking protects PII/PHI at query time with role-aware policies (partial reveal, tokenization, date shift, randomization). Masked values flow through BI tools and exports, reducing the chance of leakage—even when teams query production data.
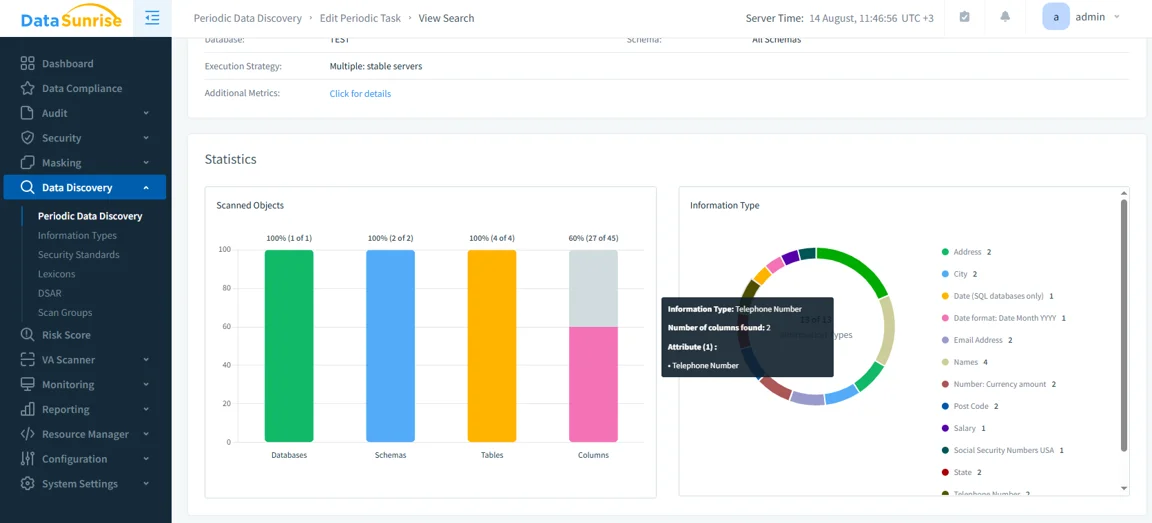
Sensitive data discovery
Sensitive data discovery continuously scans schemas to classify fields such as names, addresses, IDs, and card numbers. It detects new sensitive columns as models evolve and promotes findings into audit or masking rules, so coverage stays current without manual rework.
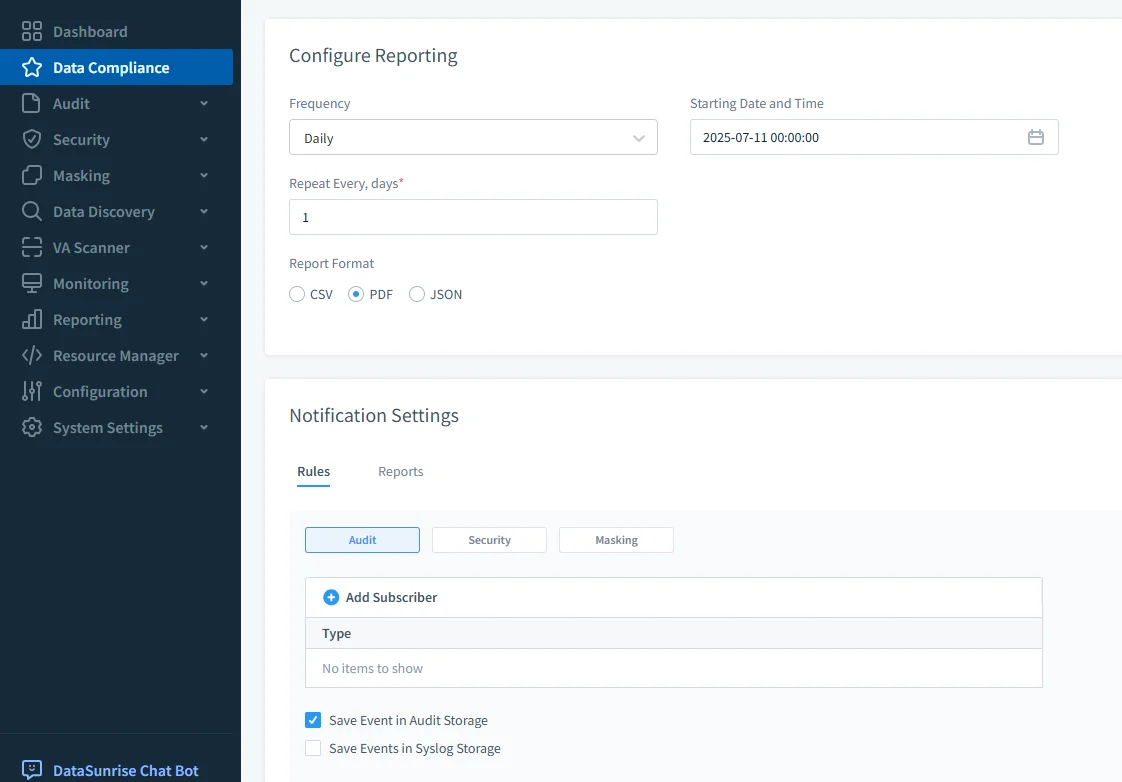
Compliance reporting
Compliance reporting generates auditor-ready reports mapped to GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. Schedule evidence packs, track rule changes over time, and export in formats reviewers accept.
All of these controls layer onto your existing .sqlaudit workflow. Keep exporting to Cloud Storage, streaming to Cloud Logging, and analyzing in BigQuery; DataSunrise adds enforcement and ready-made evidence on top of that pipeline.
Best Practices
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralize and protect logs | Export to Cloud Storage or Cloud Logging with lifecycle rules; feed SIEM or BigQuery. |
| Use role-based access | Limit who can read raw audit logs; developers should see masked values when possible. |
| Automate scope updates | Use discovery to include new schemas/tables without manual gaps. |
| Enable real-time oversight | Trigger alerts on failed logins, unusual queries, and off-hours access. |
Compliance Mapping (at a glance)
- GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX require accountability and auditable records.
- Native SQL Server Audit provides the trail.
- DataSunrise adds real-time controls, masking, discovery, and audit-ready reporting that aligns evidence with each framework.
Summary
Native SQL Server Audit on Cloud SQL gives you solid coverage. Pair it with Cloud Storage, Cloud Logging, and BigQuery for retention, search, and trend analysis. Add DataSunrise to gain real-time alerts, masking, discovery, and automated reports—so your Cloud SQL estate stays secure, auditable, and ready for compliance. You also cut manual effort, reduce blind spots across instances, and speed up investigations with a single, consistent trail.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now