Vertica Data Audit Trail
Vertica plays a central role in many analytics-driven organizations. As a result, having a reliable Vertica Data Audit Trail is essential for understanding how users interact with data and how queries affect business operations. Since Vertica powers dashboards, reporting layers, and downstream data products, a strong Vertica Data Audit Trail helps ensure transparency, detect anomalies, and meet regulatory requirements.
To put Vertica auditing into a broader governance program, it helps to rely on general resources about data compliance and regulatory frameworks. Additionally, the official Vertica documentation at provides deeper insight into native audit components. Together, these materials help align the Vertica Data Audit Trail with internal and external policies.
Why Database Audit Matters for Vertica Clusters
Vertica often serves as the analytical backbone of a modern enterprise. Consequently, departments such as finance, sales, data science, and operations rely on its insights. Therefore, when workloads include customer data, financial indicators, operational logs, or sensitive metrics, organizations must maintain full visibility into who accessed which objects and when. A structured Vertica Data Audit Trail provides that clarity.
If something goes wrong — for instance, an unexpected data export or unauthorized action — teams must answer three essential questions:
- Who accessed the database?
- Which objects or schemas were touched?
- Was this activity acceptable under audit and compliance policies?
Native Vertica logs offer some visibility. However, they rarely satisfy all the needs of auditors and security teams. As a result, many organizations use an external audit layer such as DataSunrise Activity Monitoring. It normalizes events, enriches them with context, and produces reports that simplify investigations.
Native Database Audit Capabilities in Vertica
Vertica includes several built-in audit and diagnostic tools. Consequently, administrators already have a baseline for understanding system behavior — a key part of any Vertica Data Audit Trail. Moreover, these native capabilities help detect irregularities early.
- Data Collector — records query and session metadata.
v_monitorviews — includingv_monitor.query_requests.- Diagnostic logs used for troubleshooting and operational analysis.
These components allow administrators to reconstruct cluster activity. Nevertheless, this information remains local, technical, and difficult to use for centralized governance or regulatory reporting.
How Vertica Records Query History
Vertica exposes query history through v_monitor.query_requests. Each entry includes the user, request
type, timing information, and a snippet of SQL text. Although this data is valuable, it is fragmented and
not optimized for cross-environment audit programs. Consequently, a unified audit layer becomes necessary.
Reference Architecture for a Vertica Audit Trail
A sustainable audit framework goes beyond manual queries against system views. Instead, it relies on a dedicated architecture around Vertica to maintain consistency, scalability, and long-term auditability. In practice, a common model includes the following components:
- Clients and BI tools connect to Vertica through the DataSunrise proxy.
- The proxy analyzes SQL traffic and applies audit and security policies.
- Vertica executes validated requests.
- DataSunrise stores normalized audit events in central storage.
- Security teams access audit data directly or through SIEM/SOAR tools.
This architecture simplifies oversight across multiple clusters and enables role-based audit policies. As a result, auditing becomes a shared responsibility rather than an isolated DBA task. Furthermore, it reduces the operational overhead of maintaining custom scripts.
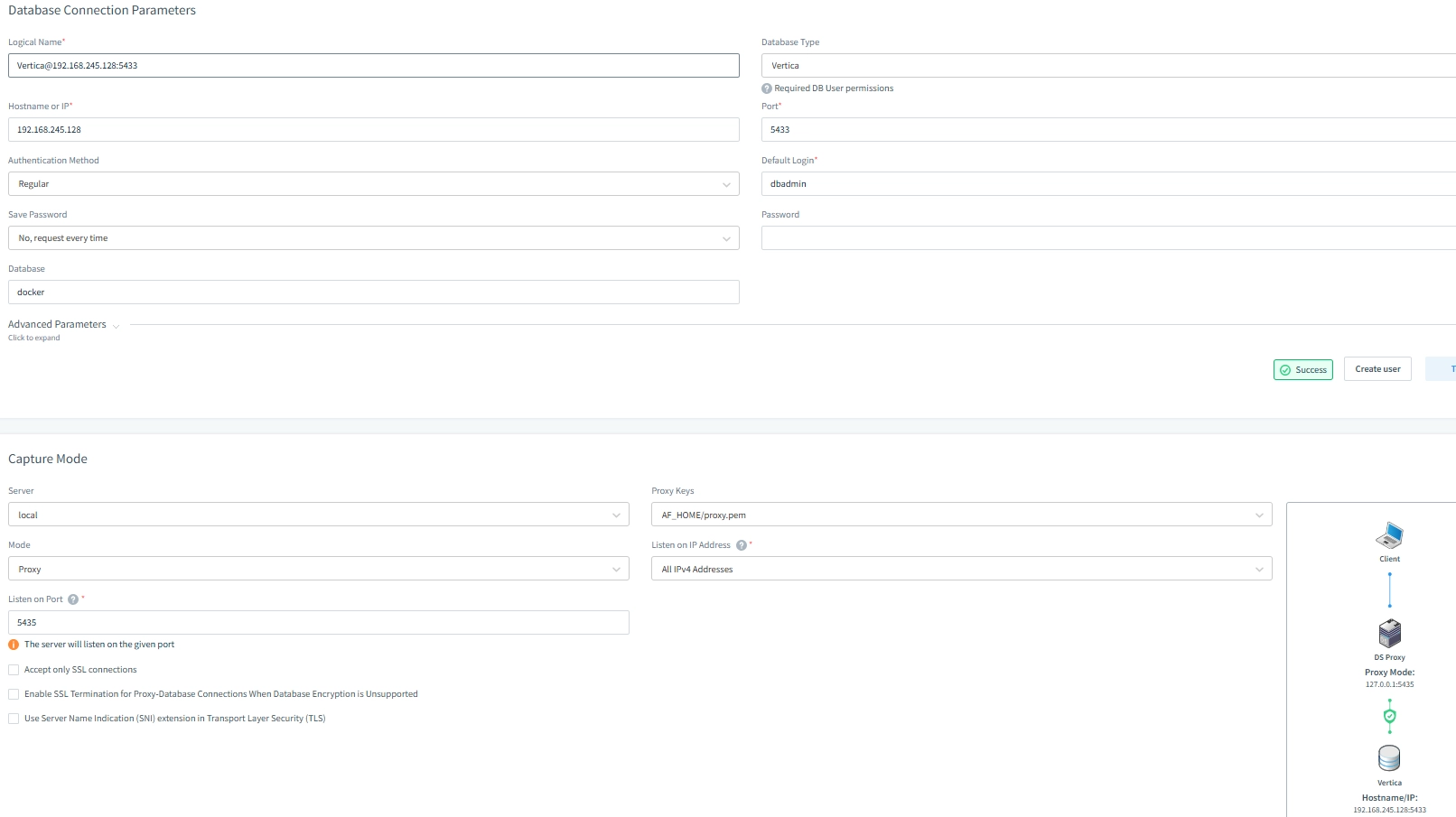
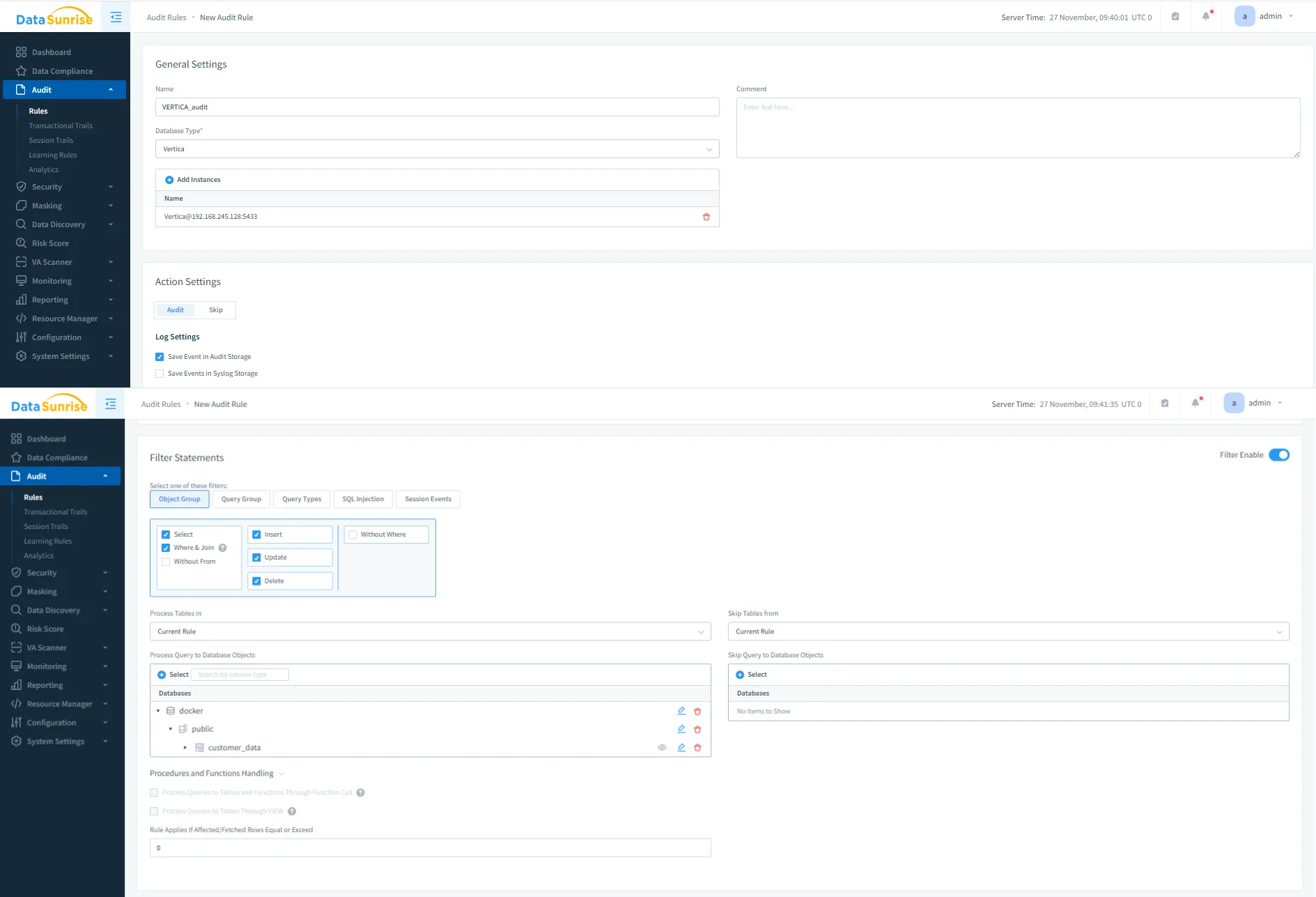
Creating a Vertica Audit Rule in DataSunrise
After deploying the proxy, organizations can create audit rules to track relevant activity patterns. As a result, teams can focus on schemas, tables, and operations, making the Vertica Data Audit Trail both clear and effective. Additionally, rule filters help reduce noise in the audit logs.
Reviewing Vertica Audit Trail Output
Captured events appear in the Transactional Trails view. This interface offers analysts a complete timeline of Vertica activity, showing what happened, who initiated it, and which audit rule recorded the event. Consequently, investigations become faster and more accurate.
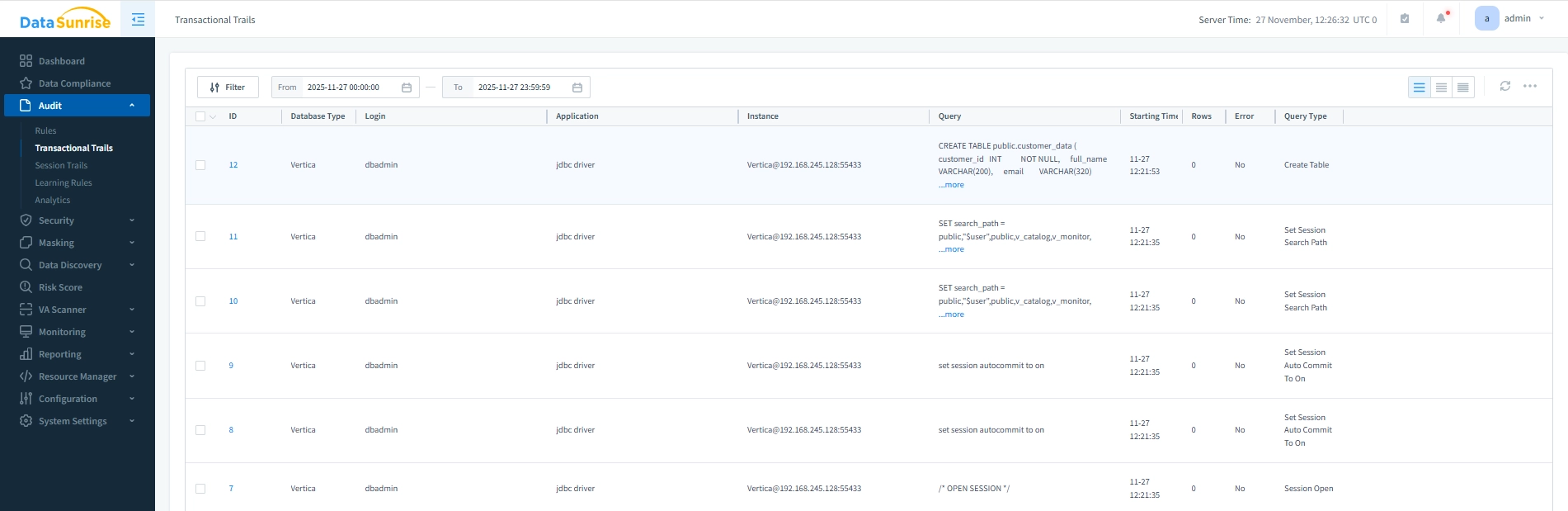
Events can be filtered by database type, rule, user, query type, or error status. Therefore, analysts can quickly isolate unusual behavior and gain deeper context than native logs provide. Moreover, trends become visible over time.
Comparing Native Vertica Logs and DataSunrise Audit Trail
Native Vertica logging and DataSunrise auditing complement one another. Together, they form a complete Vertica Data Audit Trail across environments. In contrast to Vertica-only logs, DataSunrise introduces contextual enrichment and policy control.
| Aspect | Native Vertica Logs | DataSunrise Audit Trail |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Local cluster history only | Centralized audit across databases |
| Context | SQL metadata only | User identity, application, IP, and rule context |
| Policies | Manual filtering | Rules by schema, table, or operation type |
| Compliance | Manual exports | Reports aligned with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX |
| Integrations | Custom scripts | Native SIEM/SOAR integrations |
Getting Started with Vertica Audit Trails and DataSunrise
To build a comprehensive Vertica Data Audit Trail, organizations can follow a straightforward sequence of steps. In fact, combining these steps ensures complete visibility and compliance coverage.
- Identify sensitive data using Sensitive Data Discovery.
- Deploy DataSunrise in proxy mode according to deployment guidelines.
- Create audit rules with help from the Audit Guide.
- Enable compliance reporting using Compliance Manager.
- Monitor and refine policies through Database Activity Monitoring.
Conclusion
Native Vertica logs offer essential visibility. However, a complete Vertica Data Audit Trail requires a unified auditing layer that spans users, applications, and environments. DataSunrise transforms raw Vertica events into structured audit data, dashboards, and reports. As a result, organizations enhance transparency, reduce operational risk, and maintain compliance more effectively.
To explore broader audit concepts, visit the Data Audit page. For deeper Vertica-specific details, refer to Data Audit for Vertica.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now