What Is Amazon DynamoDB Audit Trail
Amazon DynamoDB delivers consistent low-latency performance and extreme scalability, but none of that matters if you cannot prove who accessed your data, when they did it, and what exactly changed. As described in the official service documentation at https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/, DynamoDB is engineered for speed and scale, but visibility and traceability remain shared customer responsibilities. In regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, the audit trail becomes a mandatory element of operational security. Recent cloud-security findings, such as the AWS Security Maturity Report (https://d1.awsstatic.com/security-center/AWS_Security_Maturity_Model.pdf), emphasize the growing need for continuous monitoring and provable access accountability across cloud workloads. Although AWS provides several native components capable of capturing identity-driven access, configuration changes, and item-level modifications, DynamoDB has no single built-in audit subsystem. Instead, a complete audit trail must be assembled from AWS services. This article explains how the DynamoDB audit trail works and how DataSunrise provides a unified, compliance-ready audit framework powered by its Data Audit capabilities.
What Is Audit Trail?
An audit trail is a chronological narrative describing how data was accessed, modified, or interacted with, while also identifying the user, role, or service responsible for each action. In database systems, the audit trail reveals who performed specific operations, what type of activity occurred—whether it was a read, update, delete, scan, or other API call—when the event took place, including the timestamp, region, and session context, where the request originated from, such as a particular IP address, VPC source, or an assumed role session, and how the action affected the system, including item-level changes, table modifications, or structural updates.
A complete audit trail supports investigations and forensic analysis, provides regulatory evidence for frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX, exposes insider activity that may otherwise go unnoticed, and enables the detection of irregular or suspicious behavior. It also helps confirm data integrity by verifying the sequence and legitimacy of operations. A broader discussion of audit trail fundamentals is available in DataSunrise’s knowledge base at Audit Trails.
In the case of DynamoDB, this audit trail is not generated by a single tool. Instead, it is constructed by combining CloudTrail logs, DynamoDB Streams, CloudWatch signals, and AWS IAM identity data to form a unified picture of what occurred within the system—similar to the multi-source strategies used in traditional Database Activity Monitoring.
Understanding the Amazon DynamoDB Audit Trail
A DynamoDB audit trail represents the combined outputs of AWS-native logging mechanisms that collectively provide complete visibility into access patterns, data operations, and administrative changes. Because DynamoDB is serverless and schema-flexible, the audit trail depends heavily on connected AWS services that capture identity, request metadata, and item-level changes. These combined sources make it possible to track data-plane operations such as PutItem or Query, control-plane actions like table creation, identity attributes, event sequences, and behavioral anomalies across workloads. Organizations often supplement this with Data Activity History for long-term retention and investigation.
Native Services Forming the DynamoDB Audit Trail
DynamoDB does not generate a unified audit trail on its own, so AWS relies on several interconnected logging and monitoring systems to provide full visibility. Each service contributes a different layer of context, forming a complete picture only when combined. Understanding these native components is essential for designing a reliable and forensic-grade audit strategy around DynamoDB, similar to how DataSunrise explains structured auditing in its Sensitive Data Discovery and PII governance materials here.
1. AWS CloudTrail — Primary Control-Plane Audit Source
AWS CloudTrail logs administrative operations and records how identities interact with DynamoDB. It captures events related to table creation, table deletion, index modifications, backup and restore actions, encryption key usage, and IAM-based access. CloudTrail can also capture data-plane operations such as GetItem or UpdateItem, but this requires enabling Data Events explicitly. Without them, DynamoDB API calls are not fully visible, which is why CloudTrail forms the foundation of the audit trail but must be configured correctly to function as a complete forensic source.
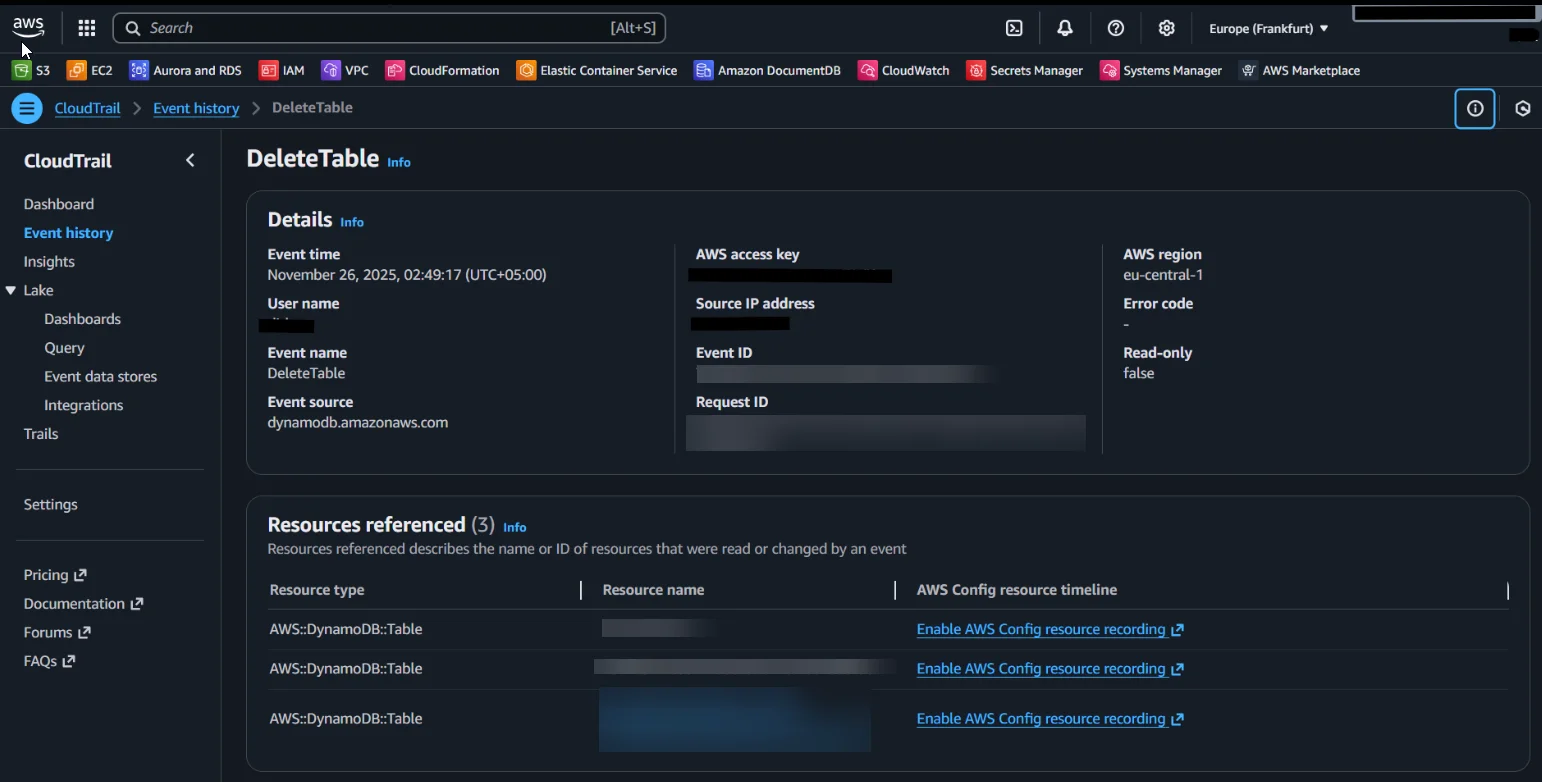
2. DynamoDB Streams — Item-Level Change History
DynamoDB Streams record fine-grained changes to items whenever they are created, updated, or deleted. Streams can include previous and new item images, which allows auditors to reconstruct exactly what changed during any write operation. This capability is essential for investigating unexpected modifications, validating regulatory evidence, and retaining detailed before/after context. Streams, however, are ephemeral and require downstream storage for long-term audit preservation.
- Streams preserve event ordering per partition key, allowing chronological reconstruction.
- Each stream record contains metadata such as sequence numbers and event source identifiers.
- Streams integrate natively with AWS Lambda for automated processing or forwarding.
- Retention is limited (default 24 hours, up to 7 days), making external archiving mandatory for audit use.
3. Amazon CloudWatch — Behavior and Performance Signals
CloudWatch adds behavioral context to the audit trail. It tracks metrics such as throttling, error rates, request volume anomalies, and latency patterns. Although CloudWatch does not independently store audit records, it helps identify suspicious trends or interactions that may require deeper analysis. Alerts and metric filters can also trigger automated responses when abnormal behavior appears.
- CloudWatch Metrics expose real-time operational patterns (read/write capacity, throttles).
- CloudWatch Logs can receive Vended Logs or custom application logs related to DynamoDB usage.
- Metric filters help identify unusual API call patterns or burst activity.
- CloudWatch Alarms integrate with SNS, Lambda, or EventBridge for automated notifications.
4. AWS IAM — Authorization Context
IAM logs and identity metadata supply the missing identity link in the DynamoDB audit trail. These records reveal which user or service assumed a role, which policies were evaluated, whether the request was allowed or denied, and which external identity provider (SAML or OIDC) initiated the session. IAM signals help connect the activity to the responsible principal.
- IAM integrates with CloudTrail to provide principal ARNs in every audit event.
- STS session details show temporary credentials, session tags, and MFA requirements.
- IAM policy evaluation logs identify which permissions were used or blocked.
- Identity-based conditions (IP restrictions, session tags, time-based rules) help trace access intent.
How DataSunrise Enhances DynamoDB Audit Trails
DataSunrise unifies CloudTrail, DynamoDB Streams, CloudWatch logs, and identity metadata into one consolidated audit system. It transforms raw AWS logs into structured, compliance-aligned audit trails with machine-learning-based analytics, real-time alerting, and masking of sensitive values. Instead of relying on multiple AWS consoles and log streams, DataSunrise provides a centralized, cross-platform view of all DynamoDB activity—a capability aligned with its core Data Security and Compliance product families.
Unified Activity Monitoring
DataSunrise correlates control-plane operations, data-plane API activity, item-level changes, identity attributes, and behavioral anomalies into a single audit record. This produces a complete, time-ordered view of how data was accessed and modified, rather than fragmenting information across separate AWS sources.
- It aggregates events from CloudTrail, Streams, CloudWatch, and IAM into a unified timeline.
- It normalizes heterogeneous AWS log formats into a consistent audit schema.
- It correlates identity, request metadata, and object-level deltas for deeper visibility.
- It surfaces anomalies through combined behavioral analysis across all log sources, leveraging techniques similar to User Behavior Analysis.
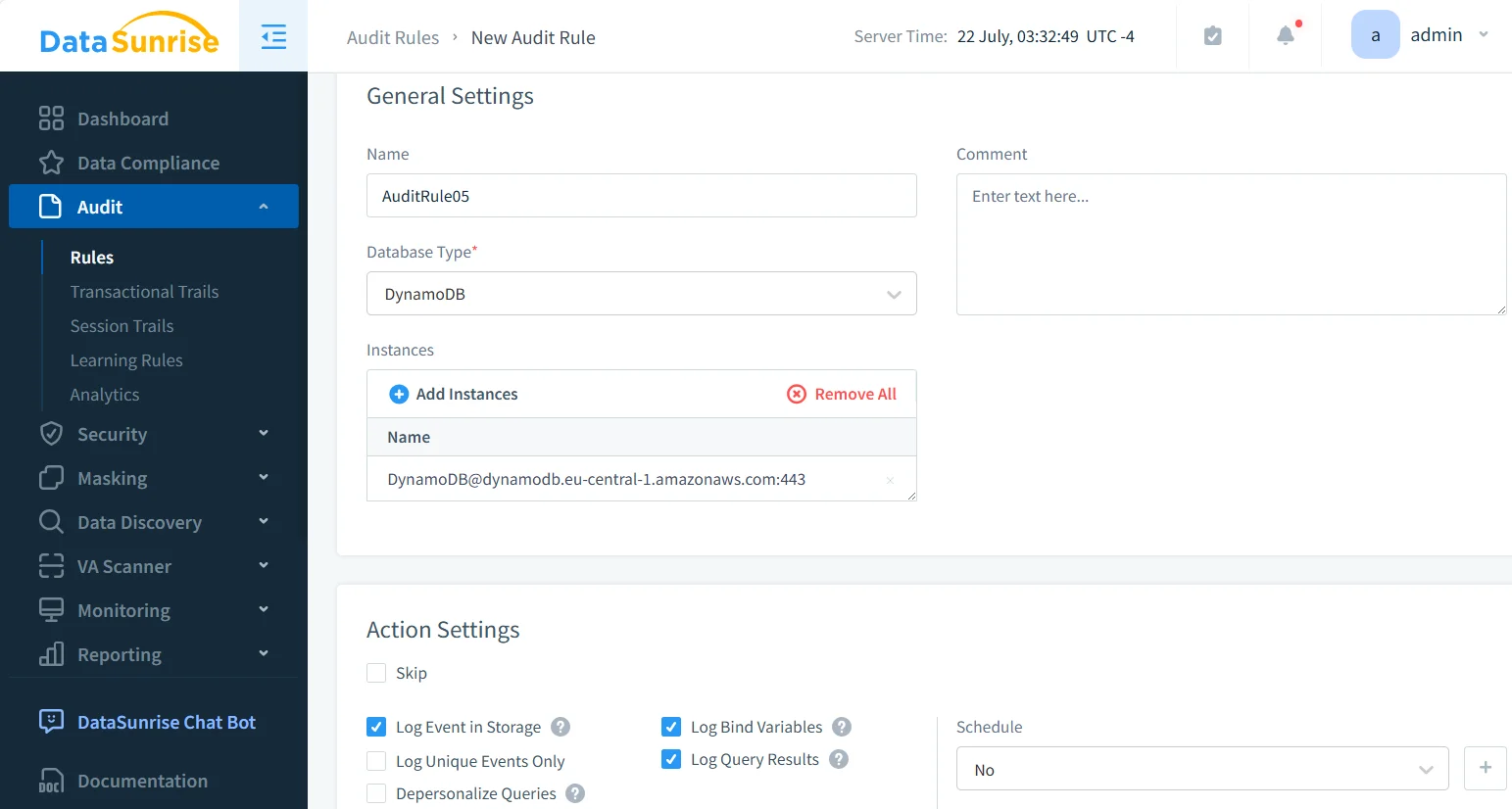
Granular Audit Rules for DynamoDB
Administrators can create highly targeted audit rules. These rules can log operations on specific tables, track updates or deletions on sensitive datasets, monitor Query or Scan requests performed by unfamiliar identities, detect spikes in API usage, and apply masking before logs are written. This brings fine-grained control similar to traditional enterprise audit subsystems, supported by DataSunrise’s Dynamic Data Masking engine.
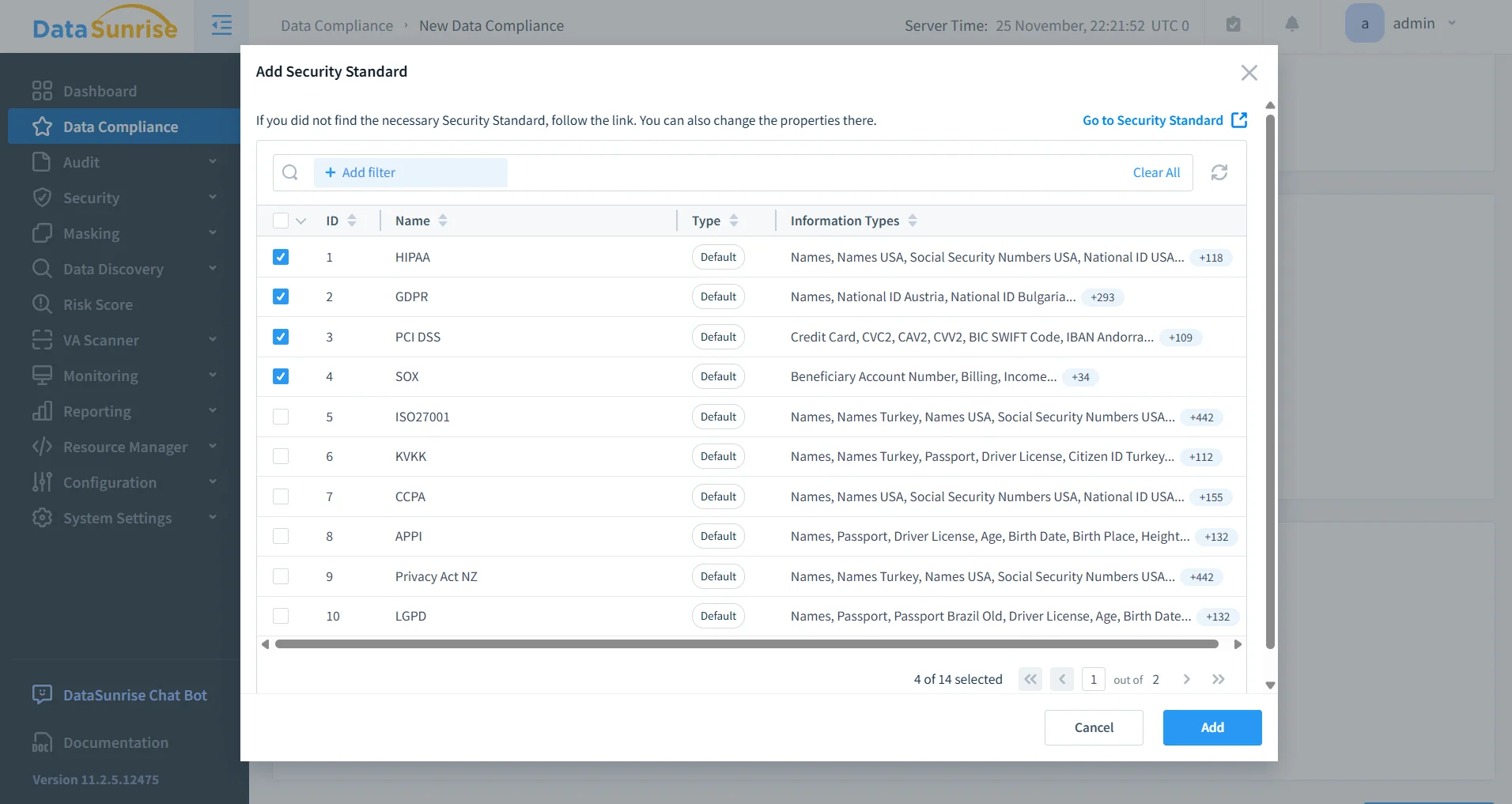
Compliance Alignment & Automated Reporting
DataSunrise automatically maps DynamoDB audit events to regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX, ISO 27001, and SOC 2. It generates centralized compliance reports, detects configuration drift, and performs continuous validation. These capabilities complement its extensive LLM & ML-based security features and support multiple deployment modes.
Business Impact
| Business Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Compliance Costs | Centralized evidence collection eliminates fragmented log review and lowers audit preparation time. |
| Faster Audit Cycles | Unified audit visibility accelerates regulatory reporting and shortens audit timelines. |
| Improved Incident Response | Correlated activity data enables quicker identification of unauthorized access and abnormal behavior. |
| Enhanced Data Governance | Consistent monitoring across DynamoDB and other platforms strengthens governance and access oversight. |
| Risk Reduction | Dynamic masking and anomaly detection limit exposure of sensitive values and reduce security threats. |
| Cross-Platform Visibility | DataSunrise extends audit capabilities across more than 40 databases and cloud platforms for enterprise-wide coverage. |
Conclusion
A DynamoDB audit trail is not produced by a single AWS tool. Instead, it is the result of CloudTrail, DynamoDB Streams, CloudWatch, and IAM logs working together. AWS provides the raw events, but DataSunrise transforms them into a coherent, compliance-ready audit system with dynamic masking, behavior analytics, unified visibility, and regulatory reporting.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now