What Is Google Cloud SQL Audit Trail
Introduction
A database audit trail is a chronological record of logins, queries, schema changes, and permission updates. In Google Cloud SQL, maintaining such an audit trail is essential for proving accountability, detecting anomalies, and meeting strict regulatory requirements.
This article explores what a Google Cloud SQL Audit Trail is and how to configure it. We’ll begin with native auditing features available in SQL Server on Cloud SQL and explain how these logs can be exported to Cloud Storage or Cloud Logging for retention and analysis.
We will then show how DataSunrise enhances these capabilities with real-time monitoring, dynamic data masking, sensitive data discovery, and automated compliance reporting. These features simplify alignment with key regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX while reducing the manual effort needed to maintain compliance.
Understanding Google Cloud SQL Audit Trail
The Google Cloud SQL audit trail is the chronological record of database operations. It captures:
- Access events: logins, session starts, authentication failures.
- Data queries: SELECT statements and data exports.
- Data modifications: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE commands.
- Schema operations: CREATE, ALTER, DROP statements.
- Permission changes: GRANT, REVOKE, and role assignments.
Such records provide accountability and ensure compliance. Without an audit trail, it becomes difficult to prove who accessed data, when, and how it was altered.
Native SQL Server Auditing in Google Cloud SQL
SQL Server Audit works seamlessly in Cloud SQL. It creates .sqlaudit files that can be exported to Cloud Storage or analyzed in BigQuery.
Create a Server Audit
CREATE SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
TO FILE (FILEPATH = '/var/opt/mssql/audit', MAXSIZE = 100 MB);
ALTER SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit WITH (STATE = ON);
Reviewing Audit Data
Once audits are enabled, administrators can query the .sqlaudit files directly within Cloud SQL. The function msdb.dbo.gcloudsql_fn_get_audit_file retrieves events in tabular form, making it easier to filter and analyze login activity, schema changes, or query executions.
SELECT TOP (200)
event_time,
action_id,
succeeded,
server_principal_name,
database_name,
statement,
object_name,
session_id,
additional_information
FROM msdb.dbo.gcloudsql_fn_get_audit_file('/var/opt/mssql/audit/*', NULL, NULL)
ORDER BY event_time DESC;
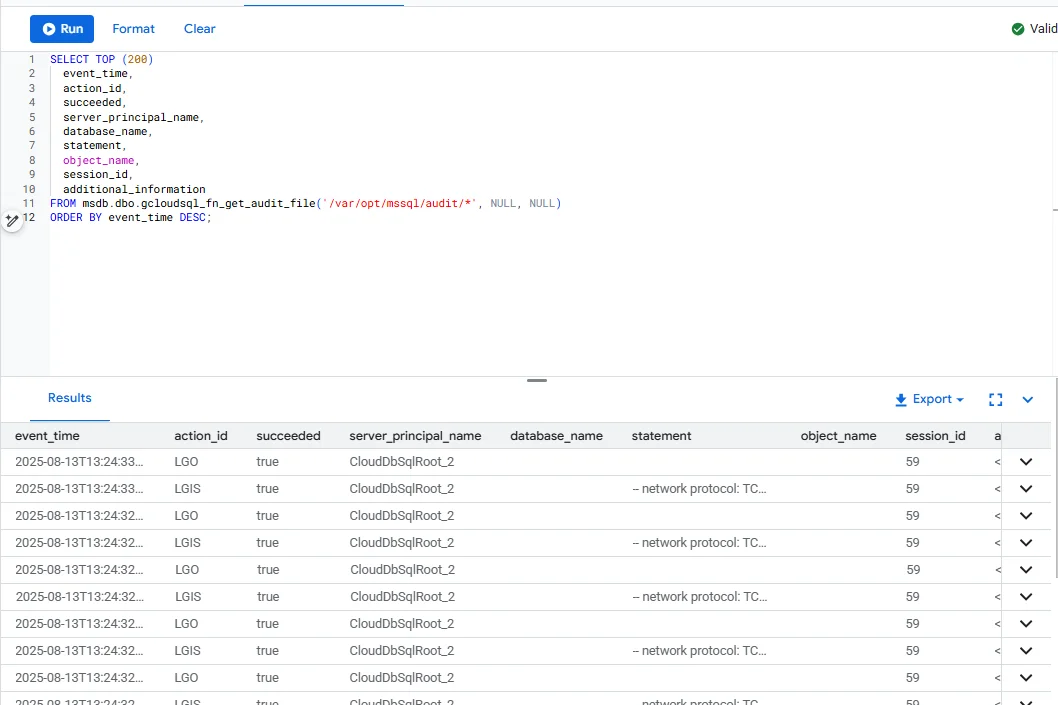
This native review capability provides quick visibility into database activity and supports forensic analysis directly from SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), Azure Data Studio, or Cloud SQL Studio.
Custom Views and Procedures
-- View: recent logins
CREATE VIEW RecentLogins AS
SELECT TOP 50 client_id, login_time, ip_address
FROM logins
ORDER BY login_time DESC;
-- Procedure: log new transaction
CREATE PROCEDURE LogTransaction
@client_id INT, @amount DECIMAL(10,2), @type VARCHAR(20)
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO transactions (client_id, amount, transaction_type, status)
VALUES (@client_id, @amount, @type, 'pending');
END
These help tailor auditing to business needs.
Where Native Tools Fall Short
Despite their usefulness, SQL Server audit features in Cloud SQL face limitations:
| Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|
| No real-time alerting | Teams only react after reviewing logs |
| Sensitive data appears in plain text | Compliance risks if logs are exposed |
| Siloed by instance | Hard to correlate events across multiple Cloud SQL servers |
| Static audit scope | New sensitive tables require manual reconfiguration |
| Minimal reporting automation | Extra work needed to generate compliance-ready reports |
Enhancing the Audit Trail with DataSunrise
DataSunrise is a database security and compliance platform designed to extend the native auditing features of Google Cloud SQL. It helps organizations monitor activity across multiple environments, protect sensitive data, and generate compliance-ready reports without heavy manual work.
By integrating DataSunrise with Google Cloud SQL, administrators gain a unified audit framework that overcomes the limitations of native tools and provides actionable security insights.
Key Features
Granular Audit Rules: Define precise audit rules for specific tables, query types, or user sessions, reducing log noise and focusing on critical events.
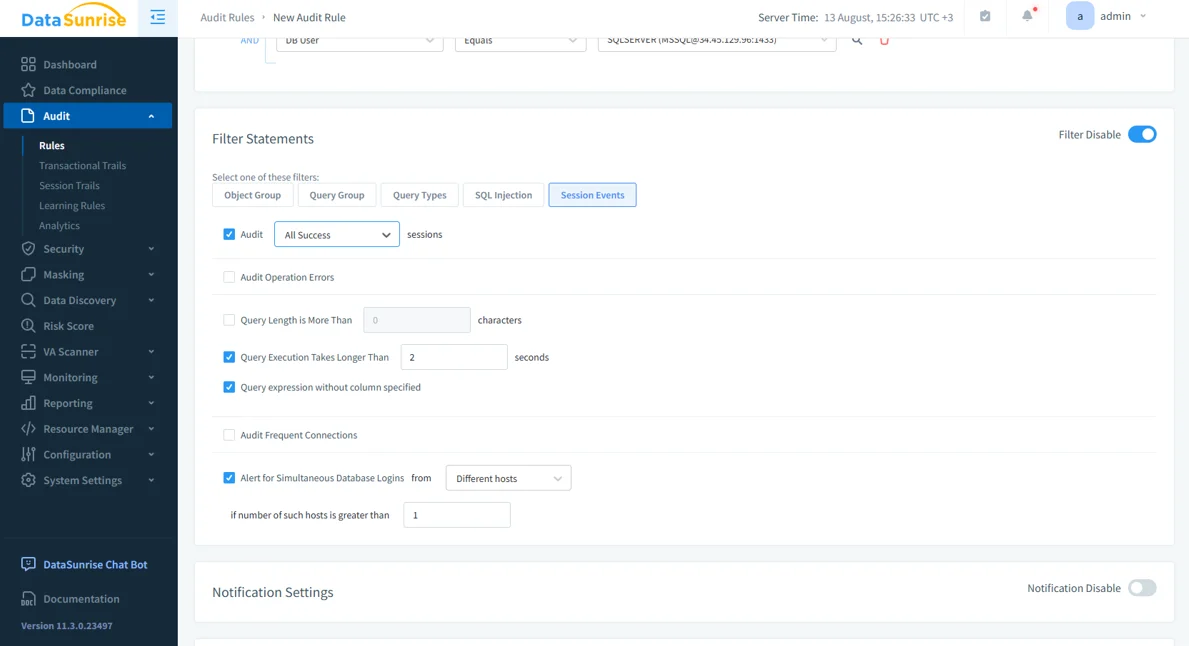
Creating an audit rule in DataSunrise. Filters allow administrators to target specific session events, long-running queries, or unusual login activity. Real-Time Monitoring: Trigger alerts through email, SIEM systems, or Slack whenever suspicious activity occurs.
Dynamic Data Masking: Protects sensitive information (PII, PHI, financial data) at query time. Authorized users see full values, while others see masked results such as
XXXX-1234.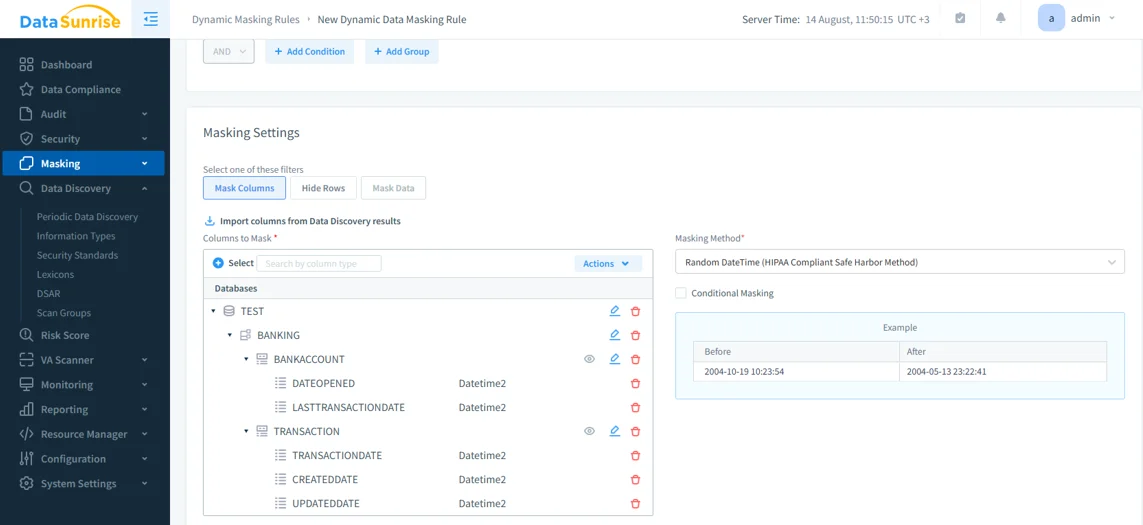
Configuring dynamic data masking in DataSunrise. Sensitive columns are masked in real time using HIPAA-compliant randomization techniques. Data Discovery: Automatically scans databases for sensitive fields and updates audit coverage when schemas change.
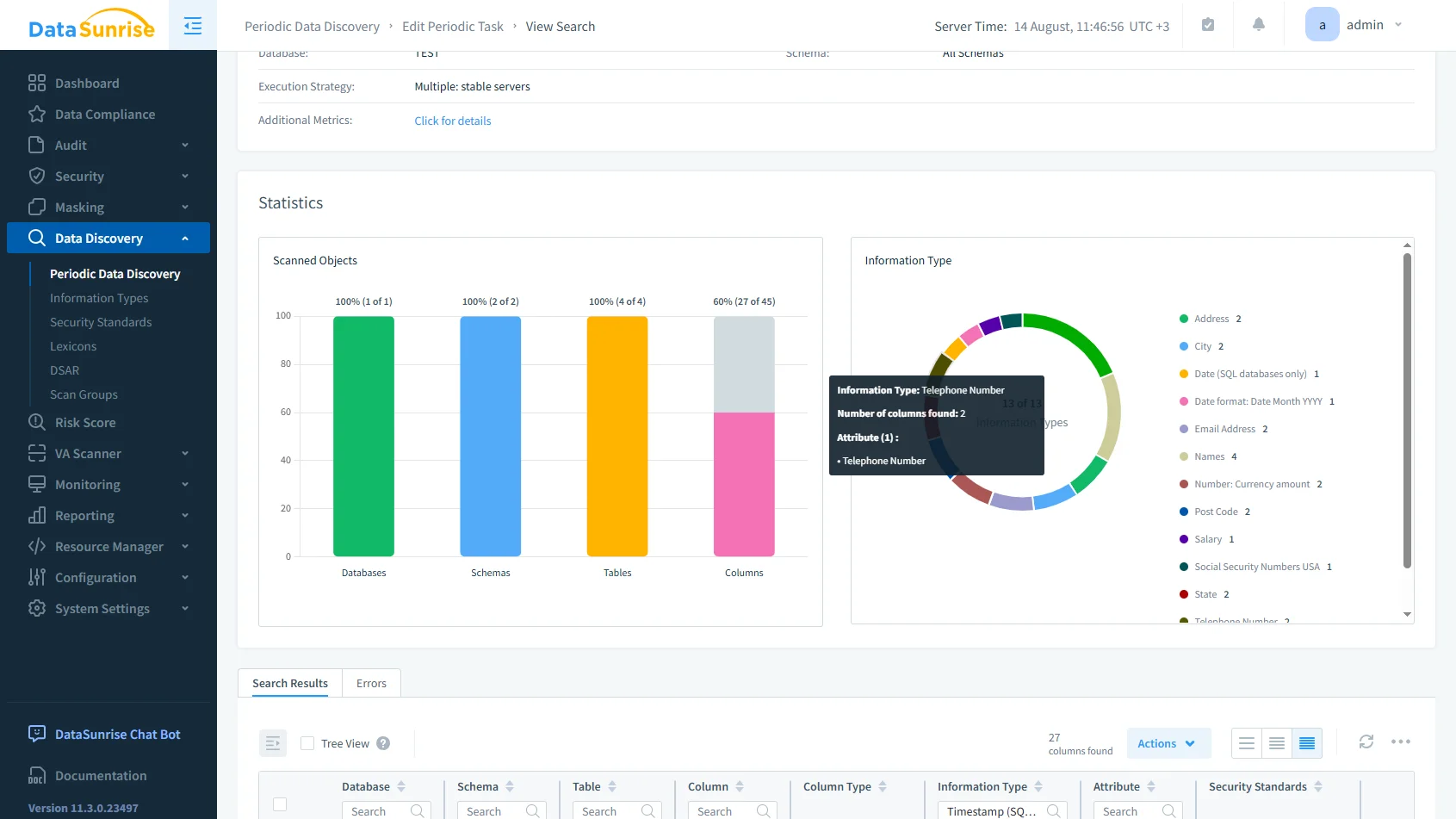
Running a periodic data discovery task in DataSunrise. The scan identifies sensitive data types across schemas, tables, and columns, supporting automated compliance. Automated Compliance Reporting: Simplifies audits by generating reports tailored to GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX requirements.
Best Practices for Google Cloud SQL Audit Trails
Building an audit trail is only the first step. To ensure it adds real value for security and compliance, organizations should follow a few practical guidelines.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralize and Protect Logs | Export audit files to Cloud Storage or Cloud Logging with lifecycle rules. This prevents data loss, supports long-term analysis, and allows DataSunrise to unify monitoring across multiple instances. |
| Use Role-Based Access | Restrict who can view or modify audit data. Compliance officers may require full visibility, while developers only see masked values to protect sensitive details. |
| Automate Scope Updates | As new tables or schemas are introduced, include them in audit coverage automatically. Data discovery tools help detect new sensitive fields without manual reconfiguration. |
| Enable Real-Time Oversight | Move beyond retrospective reviews and use real-time monitoring to trigger alerts when suspicious queries or login attempts occur, reducing response times in regulated environments. |
Conclusion
The Google Cloud SQL audit trail is more than a log—it is the foundation of accountability, compliance, and proactive security. While SQL Server’s native features provide a strong start, they lack real-time intelligence and centralized oversight.
By integrating DataSunrise, organizations gain real-time alerts, dynamic masking, automated reporting, and cross-instance visibility, creating a security framework that is audit-ready and scalable. This combination ensures compliance while reducing risk and operational overhead.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now